Utilizing a pre-designed framework for this financial document offers several advantages. It ensures consistency in reporting, simplifying comparisons across different periods. A standardized format facilitates accurate data entry and reduces the risk of errors. Furthermore, a readily available structure saves time and resources, allowing organizations to focus on analysis rather than document creation. This is particularly beneficial for small businesses or those without dedicated accounting personnel.

This foundational understanding of financial reporting lays the groundwork for exploring specific topics within the realm of financial analysis. Key areas to consider include interpreting key performance indicators, understanding the impact of various expense categories on profitability, and utilizing these insights for strategic decision-making.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is a cornerstone of effective financial reporting using a statement of revenue and expenses template. Consistency in presentation ensures comparability across different reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and informed decision-making. A standardized template predefines the structure, including line items for revenue streams, expense categories, and calculations for gross profit, net income, and other key metrics. This eliminates ambiguity and ensures that financial data is presented uniformly, regardless of who prepares the report.
Consider a business that tracks its sales revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. Without a standardized format, these figures might be presented differently each month, hindering the ability to identify meaningful trends. A standardized template ensures consistent categorization and calculation, allowing for accurate year-over-year or month-over-month comparisons. For instance, consistent reporting of marketing expenses within a dedicated category allows for analysis of its effectiveness over time and in relation to revenue generated. This enables data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and budget adjustments.
Implementing standardized formats through templates enhances the reliability and interpretability of financial information. While specific reporting requirements may vary based on industry regulations and internal needs, the underlying principle remains constant: consistent presentation fosters clarity, facilitates analysis, and promotes informed financial management. This standardization supports both internal stakeholders in their operational and strategic decision-making and external stakeholders, such as investors and lenders, in their assessment of financial health and performance. Overcoming the challenges of inconsistent data presentation enables organizations to leverage financial information as a powerful tool for growth and stability.
2. Simplified Reporting
A primary advantage of utilizing a statement of revenue and expenses template lies in its ability to simplify financial reporting. Templates streamline the process of organizing and presenting financial data, making it more accessible and understandable for various stakeholders. This simplification reduces the complexity often associated with financial statements, enabling efficient analysis and informed decision-making.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates often incorporate pre-built formulas for key calculations, such as gross profit, net income, and profit margins. This automation eliminates manual calculations, reducing the risk of errors and saving significant time. For example, a template automatically calculates gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue, ensuring accuracy and consistency across reporting periods. This allows analysts to focus on interpreting the results rather than performing repetitive calculations.
- Predefined StructureTemplates provide a predefined structure with designated sections for different revenue streams and expense categories. This structured format ensures consistency in reporting and facilitates comparisons across different periods. For instance, a template might include separate sections for operating expenses, selling expenses, and administrative expenses. This clear categorization makes it easier to track spending patterns and identify areas for potential cost savings. A consistent structure also simplifies the process of comparing current performance to previous periods or budgeted figures.
- Consolidated InformationTemplates consolidate essential financial information into a single, organized document. This eliminates the need to gather data from multiple sources, streamlining the reporting process and reducing the likelihood of discrepancies. By presenting a comprehensive overview of financial performance, templates provide a clear and concise picture of an organization’s profitability and financial health, facilitating efficient communication with stakeholders like investors or board members.
- Accessibility and ClaritySimplified reporting through templates enhances the accessibility of financial data, making it easier for non-financial professionals to understand key metrics and trends. Clear and concise presentation of information facilitates communication and collaboration across different departments within an organization. For instance, a sales team can use a simplified income statement to track revenue performance against targets, while a marketing team can analyze the impact of campaigns on overall profitability. This shared understanding of financial data supports informed decision-making at all levels.
By streamlining the reporting process and enhancing clarity, these aspects of simplified reporting contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of a statement of revenue and expenses template. This facilitates better financial management, enabling organizations to leverage financial data for strategic planning, performance evaluation, and informed decision-making. The simplified format empowers stakeholders to grasp the financial narrative effectively, contributing to enhanced transparency and accountability.
3. Error Reduction
Accuracy in financial reporting is paramount. A statement of revenue and expenses template plays a crucial role in minimizing errors, thereby enhancing the reliability of financial data. Templates achieve this through structured formats, automated calculations, and data validation features, contributing significantly to the integrity of financial analysis and decision-making.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates automate calculations for key metrics like gross profit, net income, and various ratios. This eliminates manual calculations, a common source of human error. For example, a template automatically calculates net income by subtracting total expenses from total revenues, ensuring consistency and accuracy regardless of who prepares the report. This automation reduces the risk of transposition errors, incorrect formulas, and other calculation mistakes that can significantly impact the reported financial performance.
- Data ValidationSome templates incorporate data validation features, restricting input to specific formats or ranges. This prevents the entry of invalid data, such as text in a numerical field or values outside predefined limits. For instance, a template might restrict the entry of negative values in a revenue field or enforce specific date formats. Such validation mechanisms prevent inconsistencies and ensure data integrity from the point of entry, reducing the need for subsequent error correction and improving the overall reliability of the financial data.
- Standardized Input FieldsStandardized input fields within a template guide users to enter data consistently. Clearly labeled fields for specific revenue and expense categories minimize ambiguity and reduce the likelihood of data being entered in incorrect locations. For example, a template with designated fields for “Rent Expense” and “Utilities Expense” ensures that these costs are consistently categorized, preventing misclassification errors that could distort financial analysis. This consistency promotes accuracy and comparability across reporting periods.
- Predefined Formulas and FunctionsTemplates utilize predefined formulas and functions for complex calculations, ensuring consistency and accuracy. This eliminates the need for users to manually create or modify formulas, reducing the risk of formula errors. For instance, a template might use a predefined formula to calculate depreciation expense based on a specified method and asset life. This standardization ensures that complex calculations are performed consistently across the organization, enhancing the reliability of financial reports and reducing the risk of discrepancies arising from inconsistent formula application.
By minimizing errors through these mechanisms, a statement of revenue and expenses template contributes significantly to the reliability and trustworthiness of financial information. This enhanced accuracy strengthens the foundation for sound financial analysis, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable data. The reduction in errors also streamlines the reporting process, freeing up resources for more strategic activities. Consequently, the template becomes a valuable tool for promoting financial transparency, accountability, and sound financial management practices.
4. Time Efficiency
Time efficiency is a critical factor in financial management. Utilizing a statement of revenue and expenses template significantly enhances this efficiency, streamlining processes and freeing up valuable time for analysis and strategic decision-making. Templates achieve this through automation, standardization, and consolidated reporting, allowing organizations to optimize resource allocation and focus on higher-value activities.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates automate calculations for key financial metrics, eliminating manual calculations and reducing the time spent on repetitive tasks. This automation not only saves time but also ensures accuracy and consistency in reporting. Consider a business calculating cost of goods sold (COGS). A template automatically calculates COGS based on inventory data and sales figures, eliminating the need for manual calculations and reducing the risk of errors. The time saved can be redirected towards analyzing COGS trends and optimizing inventory management strategies.
- Standardized Data EntryTemplates provide standardized input fields for revenue and expense data, streamlining the data entry process. This predefined structure eliminates ambiguity and reduces the time spent on formatting and organizing data. For example, a standardized template ensures consistent categorization of operating expenses, such as rent, utilities, and salaries. This eliminates the need for manual sorting and categorization, allowing for quicker data entry and report generation. The consistent format also facilitates comparison across different periods.
- Report Generation SpeedTemplates significantly accelerate the report generation process. Pre-built formats and automated calculations enable rapid creation of financial statements, freeing up time for analysis and interpretation. Instead of manually compiling data and formatting reports, financial professionals can generate reports with a few clicks, allowing them to focus on analyzing the results and providing valuable insights to stakeholders. This rapid reporting capability is particularly crucial for meeting deadlines and responding quickly to changing business conditions.
- Reduced Review and Revision TimeStandardized templates minimize the need for extensive review and revision. Consistent formatting and automated calculations reduce errors, leading to fewer discrepancies and less time spent on correcting mistakes. This streamlined process allows for quicker review and approval cycles, facilitating timely decision-making. For example, a template with built-in error checks and data validation features minimizes the need for manual review and correction of data entry errors, further enhancing time efficiency.
By enhancing time efficiency across these key areas, a statement of revenue and expenses template becomes a valuable tool for optimizing financial management processes. The time saved through automation and standardization can be strategically reallocated to activities such as financial analysis, strategic planning, and performance evaluation, contributing to enhanced organizational effectiveness and informed decision-making. This shift from manual tasks to strategic activities ultimately drives better financial outcomes.
5. Informed Decisions
Effective decision-making relies on accurate and accessible financial data. A statement of revenue and expenses template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting this crucial information, enabling stakeholders to gain clear insights into financial performance and make informed decisions that drive organizational success. The template serves as a foundation for data-driven decision-making, empowering stakeholders to move beyond intuition and base choices on concrete financial evidence.
- Performance EvaluationTemplates facilitate performance evaluation by providing a clear overview of revenue generation and expense allocation. By comparing actual results against budgeted figures or previous periods, organizations can identify trends, assess the effectiveness of strategies, and make necessary adjustments. For example, a decline in sales revenue highlighted by the template might prompt an investigation into market trends or competitor activities, leading to informed decisions regarding pricing strategies or marketing campaigns. Similarly, an increase in operating expenses might trigger a review of cost-control measures.
- Resource AllocationUnderstanding revenue streams and expense drivers is crucial for effective resource allocation. Templates provide insights into the profitability of different products or services and the cost-effectiveness of various operational activities. This information empowers organizations to allocate resources strategically, prioritizing investments in high-performing areas and identifying opportunities for cost optimization. For instance, a template revealing a high customer acquisition cost might prompt investment in more efficient marketing channels. Conversely, a low return on investment for a particular product line might lead to a decision to discontinue it and reallocate resources to more profitable ventures.
- Strategic PlanningStrategic planning requires a comprehensive understanding of financial performance. Templates provide the necessary data to inform strategic decisions regarding growth initiatives, expansion plans, and long-term financial goals. By analyzing historical trends and projecting future performance based on template data, organizations can develop realistic budgets, set achievable targets, and make informed decisions about investments, acquisitions, and market positioning. For example, consistent profitability demonstrated in the template might support a decision to expand into new markets or invest in research and development. Conversely, a period of sustained losses might necessitate a strategic shift in focus or a reassessment of operational efficiency.
- Risk ManagementIdentifying and mitigating financial risks is essential for organizational stability. Templates aid in risk management by highlighting potential vulnerabilities, such as declining profit margins, increasing debt levels, or unsustainable expense growth. This early identification allows organizations to implement proactive measures to mitigate these risks and protect financial health. For instance, a template revealing a shrinking profit margin might prompt a review of pricing strategies, cost control measures, or operational efficiency. This proactive approach to risk management, informed by the data presented in the template, allows organizations to navigate challenges effectively and maintain financial stability.
By providing the data necessary for these key decision-making processes, a statement of revenue and expenses template empowers stakeholders to act strategically and drive positive outcomes. The insights derived from the templates structured presentation of financial information become the foundation for informed choices, fostering financial stability, sustainable growth, and enhanced organizational performance. The ability to analyze trends, evaluate performance, and anticipate future challenges based on accurate and accessible financial data distinguishes informed decision-making from reactive responses, contributing significantly to long-term success.
6. Performance Analysis
Performance analysis relies heavily on accurate and readily available financial data. A statement of revenue and expenses template provides the structured framework necessary for effective performance evaluation. By organizing financial information into standardized categories and automating key calculations, the template facilitates in-depth analysis of revenue streams, expense drivers, and overall profitability. This analysis enables informed decision-making and drives continuous improvement.
- Trend IdentificationTemplates facilitate the identification of trends in revenue and expenses over time. By comparing data across different reporting periods, organizations can identify patterns, such as seasonal fluctuations in sales or steadily increasing operating costs. For example, consistent revenue growth over several quarters, as revealed by the template, could indicate successful market penetration. Conversely, a persistent decline in profit margins, easily tracked through the template, might signal a need to re-evaluate pricing strategies or cost control measures. Recognizing these trends enables proactive adjustments to business strategies.
- BenchmarkingTemplates provide a standardized basis for benchmarking performance against competitors or industry averages. By comparing key metrics like profitability ratios or expense percentages, organizations can assess their competitive standing and identify areas for improvement. For instance, if a company’s operating expense ratio, consistently tracked via the template, is significantly higher than the industry average, it signals potential inefficiencies. This comparison can prompt a review of operational processes and cost optimization strategies. Benchmarking allows organizations to identify best practices and strive for continuous improvement.
- Profitability AnalysisTemplates enable detailed analysis of profitability by breaking down revenue and expenses into specific categories. This granular view allows organizations to identify the most and least profitable products, services, or customer segments. For example, a template might reveal that a specific product line generates high revenue but also incurs disproportionately high production costs, resulting in a low profit margin. This insight could lead to decisions regarding pricing adjustments, cost reduction initiatives, or even discontinuation of the product. Profitability analysis guides resource allocation and strategic decision-making.
- Variance AnalysisTemplates facilitate variance analysis by comparing actual results against budgeted figures. This comparison highlights deviations from planned performance, allowing organizations to identify areas of concern and take corrective action. For instance, a significant variance between actual and budgeted marketing expenses, easily identified in the template, could indicate overspending or ineffective campaign execution. This prompts further investigation and adjustments to budget allocation or marketing strategies. Variance analysis ensures adherence to financial plans and promotes accountability.
These facets of performance analysis, facilitated by a statement of revenue and expenses template, provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health and operational efficiency. The insights derived from this analysis empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and drive continuous improvement, ultimately contributing to long-term financial sustainability and strategic success. By providing a structured framework for data analysis and interpretation, the template becomes an indispensable tool for effective performance management and strategic planning.
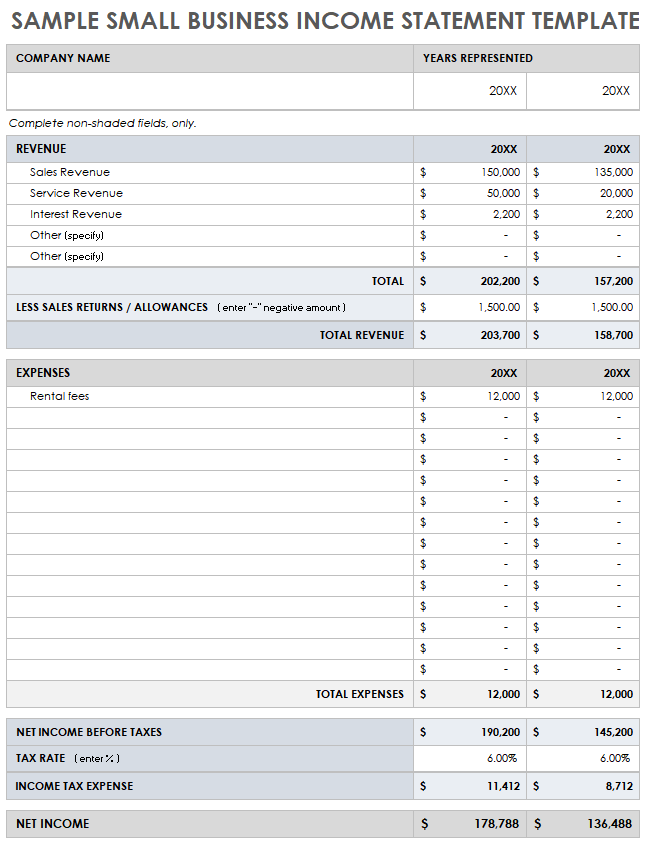
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement
A comprehensive profit and loss statement requires specific components to provide a clear and accurate picture of financial performance. These components, when organized within a standardized template, facilitate consistent reporting, efficient analysis, and informed decision-making.
1. Reporting Period: A defined timeframe, such as a month, quarter, or year, is essential for accurate performance measurement. This clearly delineated period ensures that all revenue and expenses are attributed to the correct timeframe, allowing for meaningful comparisons across different periods.
2. Revenue Streams: Detailed categorization of revenue sources, including sales, services, or investments, is crucial. This breakdown allows for analysis of individual revenue stream performance and identification of key drivers of income growth or decline.
3. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing those goods. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit and understanding the relationship between production costs and revenue generation.
4. Operating Expenses: These expenses encompass the costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Categorization into specific areas like rent, salaries, marketing, and utilities enables analysis of spending patterns and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
5. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue – COGS, gross profit represents the profit generated from core business operations before accounting for operating expenses. This metric provides a valuable indicator of production efficiency and pricing effectiveness.
6. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit – Operating Expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of the business after accounting for all operating costs. This metric provides a clear picture of the company’s ability to generate profit from its ongoing operations.
7. Other Income/Expenses: This category encompasses income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, or one-time charges. Including these items provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s overall financial performance.
8. Net Income: Representing the bottom line, net income is the final profit or loss after accounting for all revenue and expenses, including taxes and other non-operating items. This crucial metric reflects the overall financial performance of the organization during the reporting period.
Accurate and consistent presentation of these components within a structured format allows for meaningful analysis of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making and contributing to long-term financial health and stability. The template serves as a tool to understand the interplay of these components and their collective impact on an organization’s financial outcomes.
How to Create a Statement of Revenue and Expenses Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting. The following steps outline the process of developing a template tailored to specific organizational needs.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the template, such as a month, quarter, or fiscal year. Consistent reporting periods are essential for accurate trend analysis and performance comparison.
2. Structure Revenue Categories: Establish clear categories for different revenue streams. This might include sales revenue, service revenue, investment income, or other relevant income sources. Detailed categorization facilitates analysis of individual revenue stream performance.
3. Outline Expense Categories: Create a comprehensive list of expense categories relevant to the organization. This should include categories such as cost of goods sold (if applicable), operating expenses (rent, salaries, marketing, utilities), and other expenses (interest, taxes). Detailed categorization enables in-depth analysis of spending patterns and cost control.
4. Incorporate Key Calculations: Include formulas for calculating key metrics like gross profit (revenue – COGS), operating income (gross profit – operating expenses), and net income (total revenue – total expenses). Automated calculations ensure accuracy and consistency.
5. Design the Layout: Structure the template in a clear and logical format. This typically involves a table format with rows for each revenue and expense category and columns for the reporting period’s actual figures, budgeted figures, and variances. A well-designed layout enhances readability and facilitates analysis.
6. Implement Data Validation: Where applicable, incorporate data validation rules to ensure data integrity. This might involve restricting input to specific formats (numbers, dates) or setting allowable ranges for values. Data validation minimizes errors and enhances reliability.
7. Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the template with sample data to ensure accurate calculations and identify any potential issues. Refine the template based on testing results to optimize its effectiveness and usability.
8. Document and Standardize: Document the template’s structure, formulas, and data validation rules. Standardize its use across the organization to ensure consistent financial reporting and analysis. Regularly review and update the template as needed to reflect evolving business needs.
A well-designed template provides a robust framework for accurate and efficient financial reporting, facilitating informed decision-making and driving organizational success. Regular review and refinement ensure its ongoing effectiveness and relevance to evolving business requirements.
Profit and loss templates provide a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Standardized reporting, facilitated by these templates, enables consistent tracking of revenue and expenses, leading to accurate calculations of key metrics such as gross profit, operating income, and net income. Error reduction through automated calculations and data validation ensures data integrity, while simplified reporting enhances accessibility for various stakeholders. The efficiency gained through automated processes frees up valuable time for analysis and strategic decision-making, enabling organizations to leverage financial data for informed choices regarding resource allocation, performance evaluation, and risk management. Ultimately, utilizing these templates empowers organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health, driving operational efficiency and long-term sustainability.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate, accessible, and actionable information. Leveraging the structure and functionality offered by these templates allows organizations to transform raw financial data into a powerful tool for strategic decision-making and sustainable growth. Consistent application and refinement of these reporting practices position organizations to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape, optimize resource allocation, and achieve long-term financial objectives. The ability to analyze trends, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks based on reliable financial data is paramount to sustained success in any economic climate.


