Utilizing such a structure offers several advantages. It simplifies the process of compiling financial data, reducing the likelihood of errors and omissions. Standardization facilitates analysis and comparison, both internally against previous periods and externally against industry benchmarks. Furthermore, it can serve as a crucial communication tool for stakeholders, providing a clear and concise overview of financial health.

The following sections will delve into the specific components of these reports, offering practical guidance on their creation and interpretation. Topics covered will include revenue recognition, cost categorization, and the calculation of key performance indicators. Examples will be provided to illustrate best practices and common pitfalls to avoid.
1. Standardized Structure
Standardized structure is a cornerstone of effective financial reporting using a profit and loss statement template. This structure ensures consistency and comparability of financial data across different reporting periods. A standardized template typically includes predefined sections for revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other income/expenses. This consistent layout enables stakeholders to readily locate and interpret key financial figures, facilitating informed decision-making. For example, consistent placement of operating expenses allows for trend analysis and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
The benefits of a standardized structure extend beyond internal analysis. It simplifies external audits and comparisons with industry benchmarks. Consistent categorization of revenues and expenses allows for accurate benchmarking against competitors and identification of areas for improvement. Furthermore, standardized reporting fosters transparency and builds trust with investors and lenders, who can rely on the consistent presentation of financial information. Consider a scenario where a company changes the categorization of its expenses each quarter. This lack of standardization would make it difficult for investors to track performance and assess risk.
In conclusion, standardized structure within a profit and loss statement template promotes clarity, consistency, and comparability. This structure facilitates both internal analysis and external communication, contributing significantly to sound financial management and informed decision-making. Challenges may arise when adapting a standardized template to unique business needs, requiring careful consideration and potential customization while maintaining the core principles of standardized reporting.
2. Pre-built Formulas
Pre-built formulas within a profit and loss statement sample template significantly enhance accuracy and efficiency in financial reporting. These formulas automate calculations, minimizing the risk of manual errors that can occur with traditional spreadsheet-based approaches. A template might include formulas for calculating gross profit (revenue – cost of goods sold), operating income (gross profit – operating expenses), and net income (operating income – other expenses + other income). Automating these calculations ensures consistency and reliability in reported figures, contributing to the overall integrity of the financial statement.
Consider a scenario where a company manually calculates its gross profit margin. A simple error in data entry or calculation could lead to misrepresented profitability. Pre-built formulas eliminate this risk, automatically calculating key metrics based on entered data. This automation not only saves time but also allows for greater focus on analysis and interpretation of the results. Furthermore, standardized formulas ensure compliance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), contributing to the reliability and auditability of financial statements.
In summary, incorporating pre-built formulas in a profit and loss statement template strengthens financial reporting by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. This automation frees up valuable time for analysis and strategic decision-making, contributing to a more robust understanding of financial performance. While templates offer pre-built formulas, understanding the underlying calculations remains crucial for interpreting results effectively and adapting the template to specific business contexts, including adjustments for non-standard revenue or cost structures.
3. Clear Data Entry Fields
Well-defined data entry fields within a profit and loss statement sample template are crucial for accurate and efficient financial reporting. Clear, unambiguous fields guide users in inputting data correctly, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring data integrity. This clarity contributes directly to the reliability of the generated financial statement and its subsequent interpretation.
- Descriptive Labels:Descriptive labels clearly indicate the type of data required for each field. For instance, a field labeled “Revenue from Product A” is more informative than a simple label like “Revenue.” This specificity reduces ambiguity and ensures data is entered into the correct categories. Accurate categorization is fundamental for generating meaningful reports and analyzing performance trends. Mislabeled or ambiguous fields can lead to incorrect data entry and misrepresented financial results.
- Data Validation Rules:Data validation rules restrict the type of data that can be entered into a field. For example, a field for “Number of Units Sold” might only accept numerical values. These rules prevent input errors, such as entering text into a numerical field, ensuring data integrity and minimizing the need for manual error checking. Enforcing data validation strengthens the reliability of the financial data and reduces the risk of reporting inaccuracies.
- Consistent Formatting:Consistent formatting across all data entry fields enhances readability and reduces the likelihood of errors. Using a consistent date format (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD) or currency format (e.g., $XXX.XX) throughout the template minimizes confusion and ensures uniformity in data presentation. Consistent formatting also simplifies data analysis and comparison across different periods or departments.
- Logical Grouping:Logically grouping related data entry fields improves workflow efficiency and reduces cognitive load. For instance, grouping all revenue-related fields together or all expense-related fields together facilitates a more streamlined data entry process. This logical grouping also enhances the template’s usability and reduces the likelihood of data being entered into the wrong section.
In conclusion, clear and well-structured data entry fields are essential components of an effective profit and loss statement template. They contribute significantly to data accuracy, reporting efficiency, and the overall reliability of financial analysis. While template design provides a framework, ongoing review and refinement of data entry fields are necessary to adapt to evolving business needs and maintain accuracy in financial reporting. This iterative process ensures the template remains a relevant and reliable tool for financial management.
4. Customizable Categories
Customizable categories within a profit and loss statement sample template offer essential flexibility, allowing businesses to tailor the template to their specific operational needs and industry requirements. This adaptability ensures the template accurately reflects the unique financial structure of each organization, rather than imposing a rigid, one-size-fits-all approach. A software company, for example, might require categories for “Software Licensing Revenue” and “Software Development Expenses,” while a retail business might need categories like “Cost of Goods Sold” and “Retail Space Rental Expense.” Without customizable categories, these specific revenue and expense streams would be difficult to track and analyze effectively.
The ability to customize categories facilitates more granular analysis of financial performance. A restaurant, for instance, could categorize food costs into “Meat,” “Produce,” and “Dairy,” allowing management to track cost trends within each category and identify potential areas for optimization. This level of detail would be unavailable with generic expense categories. Furthermore, customizable categories enable alignment with industry-specific reporting standards. Construction companies, for example, often require detailed reporting on materials, labor, and equipment costs, which can be accommodated through tailored categories within the profit and loss template. This alignment simplifies external reporting and benchmarking against competitors.
In summary, customizable categories enhance the utility and relevance of a profit and loss statement template. They provide the flexibility needed to accommodate diverse business models and industry requirements, enabling more accurate and insightful financial analysis. While customization offers significant advantages, maintaining a structured chart of accounts and adhering to consistent categorization principles are crucial for ensuring data integrity and comparability over time. Successfully implemented, customizable categories become a powerful tool for driving informed financial decision-making and enhancing business performance.
5. Automated Calculations
Automated calculations represent a critical feature within a profit and loss statement sample template, significantly impacting both the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting. By automating calculations, the template eliminates the need for manual computations, reducing the risk of human error and freeing up valuable time for analysis and interpretation of results. Consider the calculation of gross profit, a key performance indicator. A template with automated calculations automatically subtracts the cost of goods sold from revenue, ensuring accuracy and consistency regardless of the data volume. This automation eliminates the potential for transposition errors or incorrect formulas that can occur with manual calculations, especially with large datasets.
The impact of automated calculations extends beyond simple arithmetic. More complex calculations, such as calculating net profit margin or operating expense ratios, are also handled automatically. This feature allows businesses to quickly generate key performance indicators and track trends over time. For example, a template can automatically calculate and display month-over-month changes in operating expenses, enabling timely identification of cost increases and prompting investigation. Furthermore, automated calculations contribute to data integrity by ensuring calculations are performed consistently across reporting periods. This consistency is essential for comparing performance and making informed business decisions.
In conclusion, automated calculations within a profit and loss statement template significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting. By reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency, these automated processes allow businesses to focus on analyzing financial performance, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions. While automation provides significant benefits, understanding the underlying formulas and calculations within the template remains essential for effective interpretation and analysis. Regular review and validation of automated calculations are also crucial for maintaining data integrity and adapting to changing business requirements.
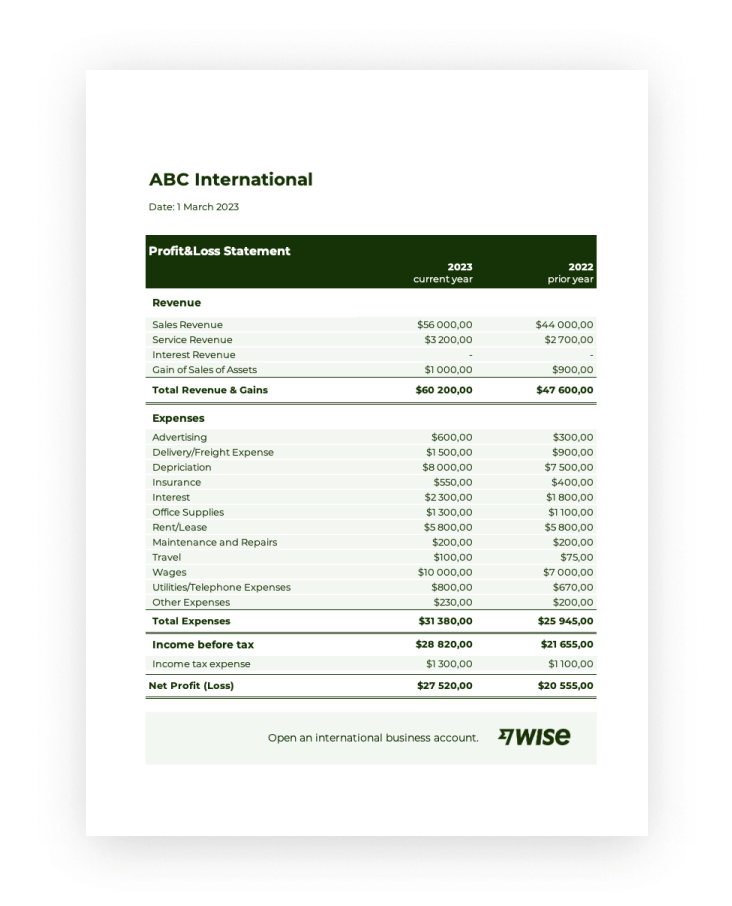
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Effective financial reporting relies on well-structured documents. Key components of a profit and loss statement template ensure comprehensive and standardized financial data presentation.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from business operations, typically categorized by source. Accurate revenue recognition is crucial for a clear understanding of financial performance. Clear categorization allows for analysis of revenue streams and identification of growth opportunities.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit. Understanding COGS helps manage production costs and pricing strategies.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as revenue minus COGS, gross profit indicates the profitability of core business operations. Analyzing gross profit trends reveals insights into pricing effectiveness and production efficiency.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Categorization of operating expenses (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing) enables detailed cost analysis. Managing operating expenses is crucial for profitability and resource allocation.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of the business before considering non-operating income and expenses. Monitoring operating income helps assess the efficiency of core business operations.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section includes income and expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income or investment gains/losses. Inclusion of other income and expenses provides a comprehensive view of financial performance beyond core operations.
7. Net Income/Loss: This bottom-line figure represents the overall profit or loss after accounting for all revenues and expenses. Net income/loss is a crucial indicator of overall financial health and sustainability. Analyzing net income trends helps assess long-term financial viability.
A well-designed profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for capturing these key components, enabling accurate, consistent, and insightful financial reporting. This standardized approach facilitates performance analysis, informs strategic decision-making, and promotes transparency for stakeholders.
How to Create a Profit and Loss Statement Sample Template
Creating a profit and loss (P&L) statement template requires careful consideration of key components and structural elements. The following steps outline the process of developing a robust and effective template.
1. Define Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the template, whether it’s a month, quarter, or year. A clearly defined reporting period ensures consistency and comparability across financial reports.
2. Establish Key Categories: Determine the main categories for revenue and expenses relevant to the business. These categories should align with the organization’s chart of accounts and provide sufficient detail for analysis.
3. Structure the Template: Organize the template logically, starting with revenue, followed by cost of goods sold (if applicable), gross profit, operating expenses, operating income, other income/expenses, and finally, net income/loss. This structure ensures a clear and consistent flow of information.
4. Incorporate Formulas: Embed formulas for automated calculations of key metrics like gross profit, operating income, and net income. Automated calculations enhance accuracy and efficiency, reducing the risk of manual errors.
5. Design Data Entry Fields: Create clear and concise data entry fields with descriptive labels and data validation rules. Well-defined data entry fields minimize input errors and ensure data integrity.
6. Add Formatting: Apply consistent formatting for dates, currency, and numerical values to enhance readability and professionalism. Consistent formatting also simplifies data analysis and comparison across different periods.
7. Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the template with sample data to ensure accurate calculations and identify potential errors. Ongoing review and refinement are crucial for adapting the template to evolving business needs.
8. Document and Maintain: Provide clear documentation explaining the template’s structure, formulas, and data entry requirements. Regularly review and update the template to ensure accuracy and relevance.
A well-designed template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting, enabling effective performance analysis, informed decision-making, and enhanced stakeholder communication. Regular review and adaptation are essential for maintaining relevance and accuracy as business needs evolve.
A profit and loss statement sample template provides a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Standardized structure, pre-built formulas, clear data entry fields, customizable categories, and automated calculations contribute to accurate, efficient, and insightful reporting. Leveraging such a template enables businesses to analyze revenue streams, manage costs, and track profitability effectively. From revenue recognition and cost of goods sold to operating expenses and net income, a comprehensive template facilitates a thorough understanding of the financial health of an organization.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate and accessible data. Adopting a robust profit and loss statement template empowers organizations to move beyond basic data collection and engage in meaningful financial analysis. This analysis informs strategic decision-making, drives operational efficiency, and ultimately contributes to long-term financial sustainability. Regular review and refinement of the template, adapting it to evolving business needs, ensure its continued effectiveness as a vital tool for financial success.


