Utilizing such a structure offers several advantages, including simplified budgeting and forecasting, improved financial analysis, and easier identification of potential cost-saving opportunities. This organized approach to financial record-keeping promotes transparency and accountability, which is crucial for businesses, individuals, and organizations of all sizes. Furthermore, a standardized format can streamline tax preparation and facilitate communication with financial stakeholders.

This understanding of structured financial record-keeping serves as a foundation for exploring key topics such as budgeting techniques, financial analysis methods, and strategies for improving profitability. Further exploration will delve into the specific components and applications of these frameworks in diverse financial contexts.
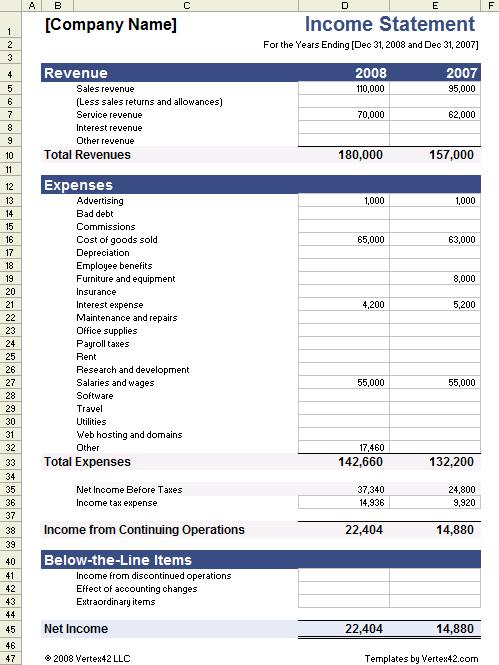
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is crucial for effective financial record-keeping. Within the context of income and expense statements, a consistent structure ensures data comparability across periods and facilitates meaningful analysis. This standardization allows stakeholders to quickly grasp key financial information and make informed decisions.
- Consistent LayoutA consistent layout ensures data is presented uniformly, regardless of the specific figures. This involves using the same structure for income sections, expense categories, and summary calculations. For example, consistently placing revenue at the top, followed by expenses, and concluding with net income/loss ensures readability and comparability across multiple statements.
- Clear LabelingClear and descriptive labels for each income and expense category eliminate ambiguity. For instance, instead of “Sales,” use more specific labels like “Product Sales” and “Service Sales.” This granularity improves transparency and allows for more precise analysis of revenue and expenditure trends.
- Date ConventionsAdhering to specific date conventions, such as using a consistent date format (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD) and clearly indicating the reporting period (e.g., “For the Month Ended June 30, 2024”), prevents confusion and ensures accurate temporal analysis. This allows for effective tracking of financial performance over time.
- Currency DenominationExplicitly stating the currency used (e.g., USD, EUR) avoids potential misinterpretations, especially in international contexts. Consistent currency denomination is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis, particularly when dealing with multiple currencies or international transactions.
These standardized elements ensure clarity, consistency, and comparability in financial reporting. Utilizing a standardized format within a template simplifies the process of creating and interpreting financial statements, leading to more informed financial decisions.
2. Categorized Income
Categorized income is a fundamental component of a well-structured income and expense statement template. Without categorization, revenue streams remain undifferentiated, hindering meaningful financial analysis. Categorization allows for the dissection of revenue sources, providing granular insights into business performance. This detailed view enables effective tracking of individual income streams, facilitating informed decision-making related to resource allocation, marketing strategies, and overall business development. For instance, a business selling both products and services benefits from categorizing income into “Product Sales” and “Service Revenue.” This differentiation reveals which revenue stream contributes more significantly to overall profitability and where potential growth opportunities lie.
Consider a freelance consultant who offers writing, editing, and coaching services. By categorizing income based on these service types, the consultant can identify the most profitable service offering and adjust their business strategy accordingly. They might discover that coaching generates higher revenue than writing, prompting them to invest more time and resources in developing their coaching practice. Similarly, a retail store categorizing sales by product lines can pinpoint top-selling items and slow-moving inventory, informing inventory management decisions and optimizing sales strategies.
Categorizing income within a standardized template offers several practical advantages. It enables performance comparison across different income streams over time, identification of seasonal trends impacting specific revenue sources, and assessment of the effectiveness of various marketing campaigns targeting different customer segments. These insights are crucial for strategic planning, resource allocation, and overall business growth. Failure to categorize income leads to a blurred financial picture, obscuring potential problems and opportunities. Therefore, a robust income and expense statement template necessitates detailed income categorization as a cornerstone of effective financial management.
3. Itemized Expenses
Itemized expenses are integral to a comprehensive income and expense statement template. A generalized “Expenses” entry obscures valuable financial insights. Itemization, the process of listing individual expenditures, provides granular visibility into the cost structure of a business or individual’s finances. This detailed breakdown facilitates effective cost management, budget analysis, and informed financial decision-making. Consider a small business using a template. Listing individual expenses such as rent, utilities, marketing costs, and salaries, rather than a lump-sum expense figure, allows for targeted cost analysis. This granular approach enables the identification of areas for potential cost reduction, optimization of resource allocation, and ultimately, improved profitability.
For example, a restaurant owner using an itemized expense section can track individual food costs, labor expenses, and utility bills. This detailed view may reveal that food costs are disproportionately high compared to industry benchmarks. Such insights can prompt investigations into supplier pricing, menu engineering adjustments, or portion control measures to address the issue. Similarly, tracking marketing expenses itemized by campaign allows for assessment of campaign effectiveness and optimization of marketing spend. Without itemization, these critical insights remain hidden, hindering effective financial management.
Practical implications of itemized expenses extend beyond cost analysis. Detailed expense records simplify tax preparation, providing supporting documentation for deductions and ensuring compliance. Furthermore, itemized expenses contribute to accurate financial forecasting and budgeting. By understanding historical spending patterns across individual expense categories, businesses and individuals can develop more realistic budgets and anticipate future financial needs. The absence of itemized expenses limits the ability to understand true cost drivers, hindering effective financial planning and control. Therefore, incorporating itemized expenses within a sample income and expense statement template is essential for sound financial management.
4. Specified Period
A defined timeframe is essential for any financial statement, including income and expense statements. The specified period provides the temporal context for the reported financial data, enabling meaningful analysis and comparison. Without a clearly defined period, the information lacks relevance and comparability. Understanding the importance of this specified period within the structure of a sample income and expense statement template is crucial for accurate financial interpretation and decision-making.
- Period LengthThe length of the specified period, whether a month, quarter, or year, significantly impacts the interpretation of the financial data. A monthly statement provides a granular view of short-term performance, while an annual statement offers a broader perspective on long-term trends. Choosing the appropriate period length depends on the specific analytical needs. For example, a business monitoring cash flow might utilize monthly statements, whereas long-term investment analysis typically relies on annual data.
- Date Range ClarityPrecise start and end dates are critical for accurate record-keeping. Ambiguity in the date range can lead to misinterpretation and difficulties in comparing financial performance across different periods. Clearly stating the dates, for example, “January 1, 2024, to January 31, 2024,” eliminates confusion and ensures data integrity.
- Comparability Across PeriodsConsistent period lengths are crucial for comparing financial performance over time. Analyzing year-over-year performance requires consistent annual statements. Similarly, tracking monthly progress necessitates adherence to a monthly reporting cycle. Inconsistent periods hinder meaningful comparisons and trend analysis.
- Contextual RelevanceThe specified period provides context for understanding the financial data. For example, unusually high sales in a particular month might be explained by a seasonal promotion. Without the monthly context, this fluctuation might be misinterpreted as a sustainable growth trend. The specified period provides the necessary context for informed interpretation.
The specified period acts as a crucial framing device within a sample income and expense statement template. It provides the temporal boundaries for the financial data, enabling meaningful analysis, comparison, and informed decision-making. Without a clearly defined and consistently applied specified period, the utility of the financial statement is significantly diminished. Therefore, understanding and correctly utilizing the specified period is essential for sound financial management and analysis.
5. Calculated Totals
Calculated totals represent a critical component of a sample income and expense statement template. These totals provide a summarized view of financial performance, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp key metrics and make informed decisions. Accurate and clearly presented totals are essential for understanding profitability, identifying trends, and managing financial resources effectively. The following facets explore the significance of calculated totals within the template’s structure.
- Total RevenueTotal revenue represents the sum of all income generated during the specified period. This figure provides a top-level view of income generation, serving as a key performance indicator. For a retail business, total revenue encompasses all sales, while for a freelancer, it includes all earnings from client projects. Accurate calculation of total revenue is fundamental to assessing overall financial health.
- Total ExpensesTotal expenses represent the sum of all expenditures incurred during the specified period. This figure reflects the overall cost of operations. For a manufacturer, total expenses include raw materials, labor, and overhead costs. Accurate calculation of total expenses is essential for understanding profitability and identifying areas for potential cost reduction.
- Net Income/LossNet income/loss, calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue, represents the bottom line the overall profit or loss for the specified period. A positive net income indicates profitability, while a negative net income signifies a loss. This crucial metric informs strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
- Subtotals within CategoriesCalculating subtotals within income and expense categories provides a more granular understanding of financial performance. For example, within expenses, calculating subtotals for marketing, operations, and administrative costs allows for detailed analysis of spending patterns within each area. This granular approach enables targeted cost management and informed budget adjustments.
Accurate calculated totals are essential for extracting meaningful insights from a sample income and expense statement template. These totals, from overall revenue and expenses to net income/loss and category subtotals, provide a concise summary of financial performance, facilitating informed decision-making, strategic planning, and effective resource allocation. The absence of accurate totals renders the template ineffective as a tool for financial analysis and management. Therefore, precise calculation and clear presentation of these figures are paramount to utilizing the template effectively.
6. Actionable Insights
Actionable insights represent the ultimate objective of utilizing a sample income and expense statement template. The template itself serves as a structured tool for organizing financial data, but the true value lies in the insights derived from that organized data. These insights, characterized by their specificity, relevance, and timeliness, empower informed decision-making and drive positive change within a business or personal financial context. The connection between the template and actionable insights lies in the template’s ability to facilitate analysis and reveal trends, ultimately leading to informed actions.
Consider a retail business using a template to track sales and expenses. The template may reveal declining sales for a particular product line. This observation, in itself, is simply data. However, further analysis using the categorized income and itemized expense data within the template might reveal that declining sales correlate with increased marketing spend on a specific campaign. This correlation transforms the initial observation into an actionable insight: the marketing campaign is ineffective and requires adjustment or termination. Without the organized data provided by the template, this insight would remain hidden, potentially leading to continued wasted marketing resources. Similarly, analyzing expense trends within the template might reveal rising utility costs. This insight could prompt investigation into energy efficiency measures, potentially leading to significant cost savings. The template facilitates these insights by providing a structured framework for data analysis.
The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to translate raw financial data into strategic action. A sample income and expense statement template, when used effectively, becomes a tool for driving continuous improvement. Challenges arise when data remains merely data, lacking the context and analysis required to generate actionable insights. Overcoming this challenge requires a commitment to regular review and analysis of the data within the template, coupled with a willingness to adapt strategies based on the insights derived. The ultimate goal is to move beyond simply recording financial information and toward utilizing that information to make informed decisions that improve financial performance. This transformative process, facilitated by the template, underscores the essential connection between organized financial data and actionable insights.
Key Components of an Income and Expense Statement Template
Effective financial management relies on clear and organized financial records. An income and expense statement template provides the necessary structure for recording and analyzing financial performance. The following components are essential:
1. Reporting Period: A clearly defined timeframe, such as a month, quarter, or year, establishes the temporal context for the data. Accurate date ranges are crucial for comparing performance across periods and identifying trends. This period acts as the foundation upon which all other data points rest.
2. Revenue Streams: Categorized revenue streams provide a detailed breakdown of income sources. This categorization allows for analysis of individual income streams and identification of key revenue drivers. Clear labeling and consistent categorization ensure accurate tracking and analysis.
3. Expense Categories: Itemized expense categories offer granular visibility into spending patterns. This detailed breakdown enables cost analysis, identification of potential cost-saving opportunities, and informed budget adjustments. Accurate categorization and detailed records are essential for effective cost management.
4. Calculated Totals: Totals for revenue, expenses, and net income/loss provide a summarized view of financial performance. Accurate calculations are crucial for understanding profitability, identifying trends, and informing strategic decisions. These totals serve as key performance indicators, enabling quick assessment of financial health.
5. Supporting Documentation: While not directly part of the statement itself, supporting documentation, such as invoices and receipts, validates the recorded data and ensures accuracy. Proper documentation practices are crucial for audits, tax preparation, and maintaining financial integrity. This documentation provides the evidentiary basis for the reported figures.
These components work together to create a comprehensive financial overview, enabling informed decision-making and effective financial management. Accurate and organized data within this framework provides the foundation for sound financial strategies and contributes to long-term financial stability.
How to Create an Income and Expense Statement Template
Creating a robust income and expense statement template requires careful consideration of key components to ensure accurate financial tracking and analysis. A well-structured template provides a clear overview of financial performance and facilitates informed decision-making.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe for the statement (e.g., month, quarter, year). Clear date boundaries are crucial for accurate tracking and period-over-period comparisons. Consistent reporting periods allow for trend analysis and performance evaluation.
2. Establish Income Categories: Categorize revenue streams to provide granular insights into income sources. Examples include sales revenue, service fees, investment income, and other relevant income streams. Detailed categorization enables tracking of individual revenue streams and identification of key performance drivers.
3. Determine Expense Categories: Create detailed expense categories relevant to the specific business or individual needs. Examples include rent, utilities, salaries, marketing expenses, and cost of goods sold. Comprehensive expense categorization facilitates cost analysis and identification of potential savings opportunities.
4. Include Calculation Formulas: Incorporate formulas to automatically calculate totals for each income and expense category, as well as overall totals for revenue, expenses, and net income/loss. Automated calculations ensure accuracy and efficiency in data analysis.
5. Design the Layout: Structure the template with clear headings, subheadings, and labels for each category. A well-organized layout enhances readability and facilitates efficient data entry and analysis. Consider using a tabular format for clear data presentation.
6. Incorporate Supporting Documentation Fields: Include fields for referencing supporting documentation, such as invoice numbers or receipt IDs. This practice ensures data integrity and facilitates verification if needed. Linking data to supporting evidence strengthens financial record-keeping.
7. Test and Refine: Test the template with sample data to ensure accuracy and functionality. Refine the template based on testing results to optimize its effectiveness and usability. Continuous improvement ensures the template remains a relevant and valuable tool.
A well-designed income and expense statement template provides a structured framework for financial record-keeping, facilitating accurate analysis, informed decision-making, and effective financial management. Consistent use of a comprehensive template contributes to long-term financial stability and success.
A structured framework for organizing financial data provides a crucial foundation for understanding financial performance. Categorized income, itemized expenses, and calculated totals within a defined reporting period offer valuable insights into revenue streams, cost structures, and overall profitability. Standardized templates facilitate consistent record-keeping, enabling meaningful comparisons across periods and informed decision-making. Proper utilization of these templates, coupled with diligent data analysis, empowers stakeholders to identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and improve financial outcomes.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate and accessible data. Leveraging the structure and insights provided by a well-designed template enables proactive financial planning, informed strategic decisions, and ultimately, greater financial success. Consistent application of these principles, coupled with a commitment to ongoing analysis and adaptation, positions individuals and organizations for long-term financial stability and growth.


