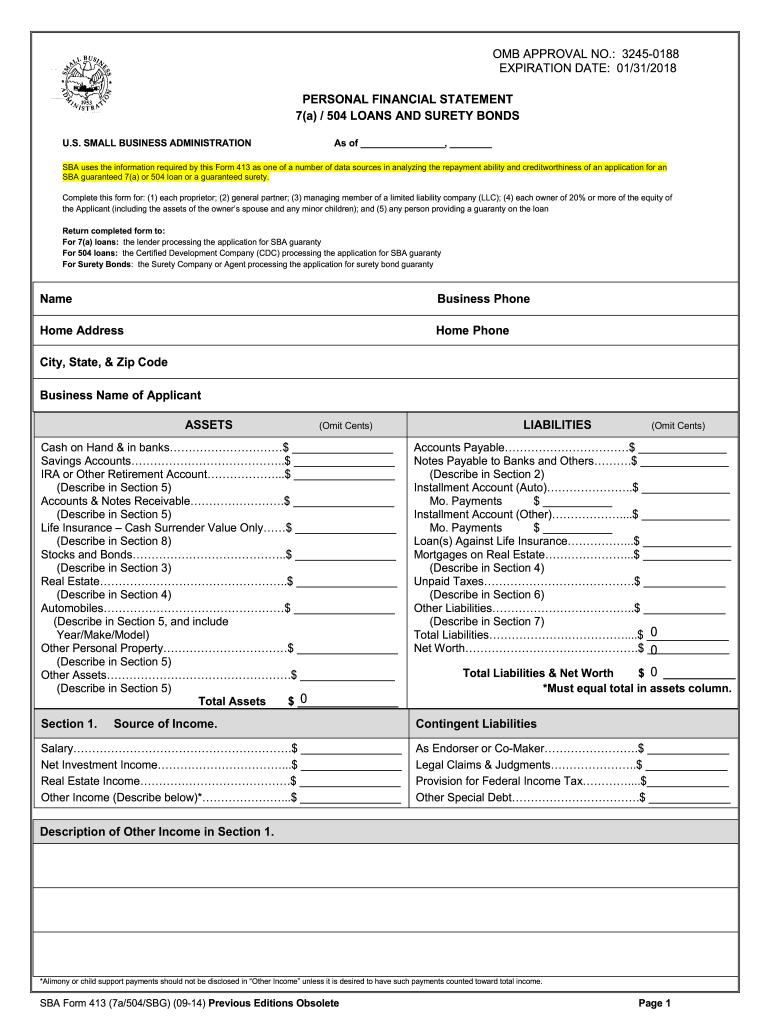
Using a standardized structure ensures consistent and transparent financial reporting, streamlining the loan application process. This clarity benefits both applicants and lenders, facilitating efficient evaluation and decision-making. A well-prepared form can significantly increase the likelihood of securing funding, demonstrating financial responsibility and preparedness.

Understanding the components and proper completion of this crucial document is essential for anyone seeking SBA assistance. The following sections will explore these aspects in detail, offering guidance and resources for a successful application process.
1. Assets
Accurate representation of assets within the SBA personal financial statement is fundamental for loan application assessment. Assets, representing items of economic value owned, play a critical role in determining an applicant’s financial strength and ability to repay borrowed funds. The statement requires comprehensive disclosure of all significant assets, categorized for clarity and thorough evaluation. These categories typically include real estate holdings, business ownership interests, checking and savings accounts, retirement funds, investment portfolios, and valuable personal property such as vehicles or jewelry.
For example, an applicant owning a rental property would list it under real estate, specifying its current market value and any outstanding mortgage balance. Similarly, ownership in a business would require disclosure of the applicant’s equity stake. Liquid assets, such as funds held in bank accounts, are also essential components, demonstrating readily available resources. Providing accurate valuations and supporting documentation for all declared assets is crucial for transparency and efficient processing of the application. Failure to accurately disclose assets can lead to application delays or rejection.
A comprehensive understanding of asset disclosure requirements is essential for successful navigation of the SBA loan process. Accurate reporting builds trust with lenders, demonstrating financial responsibility and increasing the likelihood of loan approval. This detailed disclosure provides a foundation for lenders to assess risk and make informed decisions, ultimately benefiting both the applicant and the lending institution. Neglecting or misrepresenting asset information can severely hinder the application process and damage credibility.
2. Liabilities
Accurate representation of liabilities within the SBA personal financial statement is as crucial as asset disclosure. Liabilities, representing outstanding debts and financial obligations, provide lenders with a comprehensive understanding of an applicant’s financial commitments and their potential impact on repayment capacity. The statement necessitates detailed reporting of all liabilities, categorized for clarity and thorough analysis. Common liability categories include mortgages, auto loans, student loans, credit card debt, and any other outstanding loans or lines of credit.
For instance, an applicant with an outstanding mortgage would list the remaining principal balance, monthly payment amount, and the lending institution’s details. Similarly, outstanding balances on credit cards, along with minimum payment information, need accurate reporting. A comprehensive disclosure of all liabilities, including less common ones such as personal loans or legal settlements, provides a transparent overview of the applicant’s financial obligations. This allows lenders to assess debt-to-income ratio and overall financial stability, significantly impacting the loan application outcome. Omitting or underreporting liabilities can lead to application delays, rejection, or future complications.
A thorough understanding of liability reporting requirements is essential for navigating the SBA loan application process successfully. Transparent and accurate disclosure builds trust with lenders, demonstrating financial responsibility. This meticulous reporting, combined with accurate asset disclosure, enables informed lending decisions, facilitating a more efficient and transparent loan approval process. Ultimately, accurate liability reporting benefits both the applicant and the lender by reducing risk and fostering a clearer understanding of the borrower’s financial standing. It allows lenders to assess the sustainability of the applicant’s debt load and their ability to manage additional financial obligations associated with the proposed loan.
3. Net Worth Calculation
Net worth calculation forms a cornerstone of the SBA personal financial statement. Derived by subtracting total liabilities from total assets, net worth provides a concise snapshot of an individual’s financial position. This figure holds significant weight in the loan application review process, serving as a key indicator of financial stability and repayment capacity. A positive net worth, where assets exceed liabilities, generally strengthens an application, suggesting a lower risk profile. Conversely, a negative net worth can raise concerns, potentially signaling financial vulnerability. For example, an applicant with $500,000 in assets and $200,000 in liabilities possesses a net worth of $300,000, indicating a stronger financial standing than an applicant with $200,000 in assets and $300,000 in liabilities, resulting in a -$100,000 net worth. The net worth calculation, therefore, provides crucial context for lenders evaluating loan applications, helping assess the applicant’s ability to manage debt and withstand financial fluctuations.
Understanding the relationship between net worth and loan approval is essential for prospective borrowers. While a robust net worth enhances an application, it does not guarantee approval. Lenders consider various factors, including credit history, income stability, and the viability of the proposed business venture. However, a healthy net worth provides a solid foundation, demonstrating financial responsibility and increasing the likelihood of a favorable outcome. Applicants can strengthen their financial position by strategically managing assets and liabilities. Reducing debt, increasing savings, and diversifying investments contribute to a higher net worth, improving the overall financial profile presented to lenders. This proactive approach not only enhances loan prospects but also fosters long-term financial health.
Accurate calculation and presentation of net worth within the SBA personal financial statement are critical for transparency and efficient processing. Misrepresentation or omission of financial information can jeopardize the application process and damage credibility. Therefore, meticulous record-keeping and honest reporting are paramount. A clear understanding of net worth calculation empowers applicants to present their financial standing accurately, fostering trust with lenders and contributing to a smoother and more successful loan application experience. This understanding allows applicants to engage in informed financial planning, maximizing their chances of securing necessary funding and achieving their business goals.
4. Accurate Reporting
Accuracy in completing the SBA personal financial statement is paramount. The information provided forms the basis for lender assessments of financial health and repayment capacity. Inaccuracies, whether intentional or unintentional, can lead to application delays, rejections, or even legal ramifications. For example, omitting a significant liability, such as a personal loan, misrepresents the applicant’s true debt burden and can lead to an inaccurate assessment of their ability to repay the SBA loan. Conversely, inflating the value of assets creates a misleading picture of financial strength. Accurate reporting fosters trust between the applicant and the lender, establishing a foundation for a transparent and efficient loan process.
The practical significance of accurate reporting extends beyond the immediate application process. Inaccurate information can create complications if discrepancies are discovered later. This can damage the borrower’s credibility and potentially jeopardize the loan agreement. Furthermore, consistent accuracy in financial reporting builds a positive financial history, which can be beneficial for future borrowing opportunities. Conversely, a history of inaccurate reporting can create obstacles to accessing future financing. Meticulous attention to detail and thorough verification of all information entered on the SBA personal financial statement are crucial for long-term financial success.
Maintaining accurate records throughout the application process and beyond is essential. This not only streamlines the initial application review but also provides a reliable reference point for future financial planning and interactions with lenders. Organized financial documentation supports the information provided on the statement, allowing for quick verification and minimizing potential discrepancies. Ultimately, accurate reporting, supported by comprehensive documentation, is fundamental to a successful and sustainable relationship with the SBA and lending institutions. It demonstrates financial responsibility, strengthens the application, and contributes to long-term financial stability.
5. Supporting Documentation
Supporting documentation plays a critical role in substantiating the information provided within the SBA personal financial statement template. It provides verifiable evidence for declared assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. This documentation bridges the gap between claimed financial standing and demonstrable financial reality. For instance, an applicant listing a rental property as an asset would need to provide documentation such as property deeds, mortgage statements, and rental agreements. Similarly, supporting documentation for liabilities might include loan statements, credit card bills, and other relevant financial records. This verifiable evidence allows lenders to assess the accuracy and completeness of the information presented within the personal financial statement, fostering trust and transparency.
The absence or inadequacy of supporting documentation can significantly hinder the SBA loan application process. Without verifiable proof, lenders may question the validity of the information provided, leading to application delays or rejections. A lack of supporting documentation can also raise concerns about the applicant’s organizational skills and financial management practices. For example, an applicant claiming significant business income but failing to provide corresponding tax returns or profit and loss statements may face scrutiny. Conversely, comprehensive and readily available supporting documentation streamlines the review process, demonstrating preparedness and professionalism. This preparedness can positively influence lender perceptions, contributing to a more efficient and potentially successful loan application outcome.
Understanding the crucial role of supporting documentation is essential for anyone seeking SBA assistance. Organizing and preparing these documents in advance demonstrates financial diligence and facilitates a smoother application process. A proactive approach to documentation not only strengthens the application but also contributes to a more transparent and trustworthy interaction with lenders. This meticulous preparation reflects positively on the applicant’s organizational abilities and reinforces their commitment to financial responsibility, ultimately increasing the likelihood of securing the necessary funding.
Key Components of an SBA Personal Financial Statement
A comprehensive understanding of the key components within an SBA personal financial statement is crucial for accurate and effective completion. These components provide a structured overview of an individual’s financial standing, enabling lenders to assess creditworthiness and repayment capacity.
1. Cash and Cash Equivalents: This section captures readily available funds, including checking and savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit. Accurate reporting of these liquid assets is essential for demonstrating immediate financial resources.
2. Real Estate: Real estate holdings, including primary residences, rental properties, and land, are documented in this section. Applicants must provide accurate valuations and details of any associated mortgages or liens.
3. Personal Property: Valuable personal assets, such as vehicles, jewelry, and artwork, are listed here. Providing estimated market values for these items offers a more comprehensive picture of an applicant’s overall financial holdings.
4. Business Interests: Ownership stakes in any businesses must be disclosed, including details of ownership percentage, business valuation, and any associated liabilities.
5. Liabilities: Accurate reporting of all outstanding debts, including mortgages, auto loans, credit card balances, and student loans, is crucial for demonstrating a clear understanding of financial obligations.
6. Contingent Liabilities: Potential future liabilities, such as pending lawsuits or guarantees on loans, must be disclosed to provide a comprehensive view of potential financial risks.
7. Other Assets: This section captures any assets not categorized elsewhere, such as retirement accounts, investments, and life insurance policies with cash value. Comprehensive disclosure of all assets ensures a thorough understanding of an individual’s financial resources.
Accurate and detailed reporting across these components provides a holistic view of an applicant’s financial health, enabling informed lending decisions and contributing to a transparent and efficient application process. A well-prepared statement demonstrates financial responsibility and increases the likelihood of a successful outcome.
How to Create an SBA Personal Financial Statement
Creating a comprehensive and accurate SBA personal financial statement is crucial for securing funding. The following steps provide a structured approach to developing this essential document.
1: Gather Necessary Documentation: Compile all relevant financial records, including bank statements, investment account summaries, loan documents, and tax returns. This organized approach ensures all necessary information is readily available.
2: Download the Standard Form: Obtain the official SBA Form 413 (Personal Financial Statement) from the SBA website. Using the official form ensures compliance and streamlines the application process.
3: Complete Personal Information: Accurately input personal details, including name, address, social security number, and contact information. Accurate personal information is essential for identification and processing.
4: Detail Assets: Meticulously list all assets, categorizing them appropriately (e.g., cash, real estate, personal property). Provide accurate valuations and supporting documentation for each asset. Thorough asset disclosure demonstrates financial transparency.
5: Disclose Liabilities: Provide a comprehensive account of all outstanding debts, including mortgages, loans, and credit card balances. Accurate liability reporting is crucial for assessing debt-to-income ratio.
6: Calculate Net Worth: Subtract total liabilities from total assets to determine net worth. This key figure provides a snapshot of financial standing and repayment capacity.
7: Review and Sign: Carefully review the completed form for accuracy and completeness. Sign and date the document to certify the information provided. A thorough review minimizes errors and ensures accuracy.
8: Maintain Supporting Documents: Retain copies of all supporting documentation used to complete the statement. These records are essential for verification and future reference. Organized record-keeping facilitates transparency and efficient communication with lenders.
A meticulously prepared personal financial statement, supported by verifiable documentation, strengthens loan applications and demonstrates financial responsibility. This thorough approach contributes to a transparent and efficient interaction with lenders, ultimately increasing the likelihood of securing necessary funding.
Accurate completion of the required financial statement is fundamental to the SBA loan application process. This document provides a comprehensive overview of an individual’s financial health, enabling lenders to assess creditworthiness and repayment capacity. Understanding the key components, including asset and liability disclosure, net worth calculation, and the importance of supporting documentation, is crucial for a successful application. Meticulous preparation and accurate reporting demonstrate financial responsibility and transparency, fostering trust with lenders and streamlining the review process.
The financial statement serves as a critical tool for both applicants and lenders, facilitating informed decision-making and contributing to the overall integrity of the SBA loan program. Its careful completion reflects not only an applicant’s current financial standing but also their commitment to responsible financial management, a key factor in the long-term success of any business venture. Therefore, diligent preparation of this document is an investment in both the present application and future financial endeavors.


