Utilizing such a structured document offers several advantages. It facilitates clear communication with lenders, investors, and other stakeholders. It provides a snapshot of a business’s financial health, allowing for the identification of trends, strengths, and weaknesses. This, in turn, supports better financial management and planning. Furthermore, it can streamline the loan application process, as it presents the necessary financial information in a readily accessible format.

Understanding the structure and application of this financial tool is essential for effective business management and securing necessary funding. The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components, demonstrate how to complete the document accurately, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid.
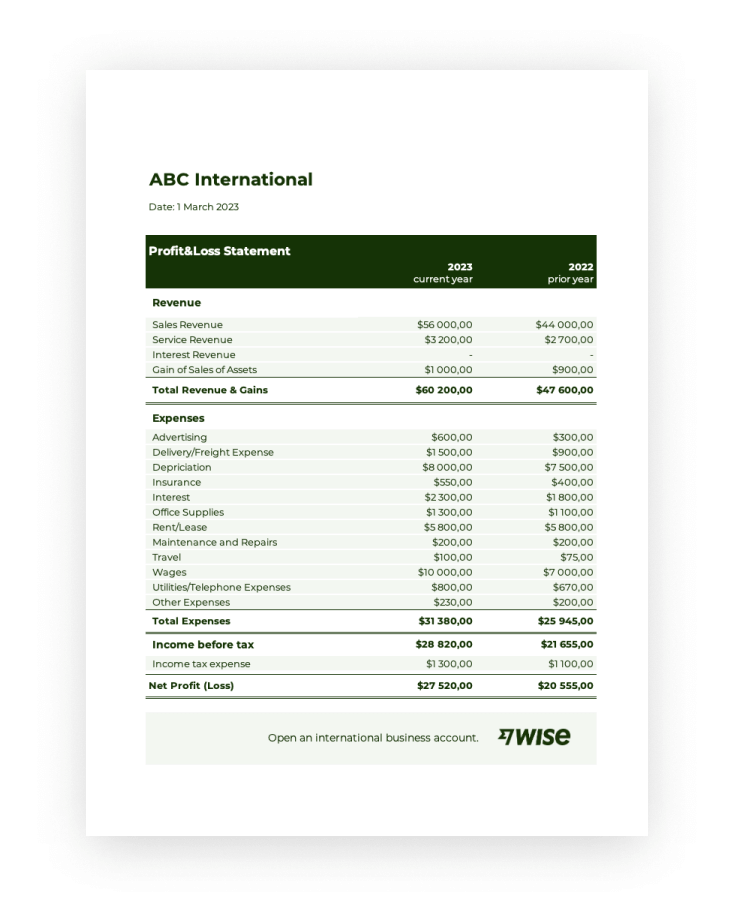
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is a cornerstone of the SBA profit and loss statement template. This uniformity ensures consistent presentation of financial data, facilitating clear communication and efficient analysis for both lenders and business owners. Adherence to a prescribed structure allows for streamlined comparisons across different businesses and time periods, crucial for evaluating financial health and making informed lending decisions.
- Uniformity of CategoriesConsistent categorization of revenue and expenses is paramount. Predefined categories, such as “Revenue from Sales” or “Operating Expenses,” ensure that similar financial data is grouped together, regardless of the specific business. This allows for direct comparisons and trend analysis across diverse industries and business models.
- Consistent Calculation MethodsStandardized calculation methods, for instance, using specific formulas for gross profit or net income, ensure consistent reporting. This eliminates ambiguity and provides a clear picture of financial performance, allowing for objective assessment. Using a consistent method helps avoid discrepancies that could arise from varying calculation approaches.
- Specified Reporting PeriodsDefining specific reporting periods, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, allows for accurate tracking of financial performance over time. Consistent timeframes enable trend analysis and comparison of performance across different periods. This allows businesses to identify seasonal fluctuations or long-term growth patterns.
- Presentation FormatA standardized presentation format, including the placement of key figures like net profit or loss, ensures that critical information is easily accessible. This facilitates quick understanding and efficient review by lenders and stakeholders. Consistent formatting minimizes the time needed to locate and interpret essential financial data.
These facets of standardized formatting contribute to the overall effectiveness of the SBA profit and loss statement template. The structure allows for clear, concise, and comparable financial reporting, enabling sound business decisions and informed lending practices. This standardized approach benefits both the applicant seeking funding and the lender assessing risk, promoting transparency and efficiency in the financial ecosystem.
2. Revenue Reporting
Accurate revenue reporting is fundamental to a comprehensive SBA profit and loss statement template. It provides the foundation for calculating profitability and demonstrating financial health to potential lenders. A clear understanding of revenue streams and their accurate representation is crucial for securing funding and making informed business decisions.
- Gross Revenue RecognitionGross revenue represents the total income generated from sales before any deductions. Accurately recording this figure is paramount, as it serves as the basis for all subsequent calculations. For a retail business, gross revenue would include all sales, irrespective of returns or discounts. Misrepresenting gross revenue can lead to a distorted financial picture and jeopardize loan applications.
- Net Revenue CalculationNet revenue is derived by subtracting returns, allowances, and discounts from gross revenue. This figure reflects the actual revenue earned after accounting for adjustments. For example, if a business offers a 10% discount, net revenue will reflect the discounted amount. Accurately calculating net revenue offers a realistic view of a business’s income.
- Revenue Stream IdentificationIdentifying distinct revenue streams is essential for a detailed understanding of business performance. If a business sells both products and services, each category should be reported separately. This allows for analysis of each stream’s contribution to overall revenue and informs strategic decision-making. It can highlight areas of strength and identify underperforming segments.
- Revenue TimingProperly timing revenue recognition is crucial for accurate financial reporting. Revenue should be recorded when earned, not necessarily when cash is received. For example, if a service is rendered in one month but payment is received the following month, revenue should be recorded in the month the service was provided. This ensures accurate reflection of financial performance within the correct accounting period.
These elements of revenue reporting contribute significantly to the overall accuracy and integrity of the SBA profit and loss statement template. Accurate and detailed revenue information is essential for demonstrating financial stability and viability to potential lenders, ultimately increasing the likelihood of loan approval and supporting sound financial management practices. Misrepresenting or omitting revenue information can lead to rejection of loan applications and hinder effective business planning.
3. Expense Categorization
Accurate and detailed expense categorization is critical within an SBA profit and loss statement template. Proper categorization provides a clear picture of where funds are allocated, enabling informed financial analysis and decision-making. This detailed breakdown of expenditures is essential for assessing business profitability, identifying areas for potential cost savings, and demonstrating responsible financial management to potential lenders.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by a business. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. For a manufacturer, COGS would include the cost of raw materials and labor directly involved in production. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit and demonstrating efficient resource utilization.
- Operating ExpensesOperating expenses encompass the costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of a business. These include rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. For a retail store, rent, staff salaries, and advertising costs fall under operating expenses. Tracking these expenses allows for insights into operational efficiency and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
- Interest ExpenseInterest expense reflects the cost of borrowing money. This includes interest paid on loans, lines of credit, and other forms of debt financing. Tracking interest expense helps assess the impact of debt on profitability and informs decisions regarding financing strategies. Accurately reporting this expense is crucial for demonstrating financial responsibility.
- Depreciation and AmortizationDepreciation and amortization account for the decrease in value of assets over time. Depreciation applies to tangible assets like equipment, while amortization applies to intangible assets like patents. Including these expenses provides a more accurate reflection of the true cost of doing business and allows for better long-term financial planning. Understanding this expense category is essential for accurate profit calculation and asset management.
Meticulous expense categorization within the SBA profit and loss statement template provides valuable insights into a business’s financial health. By accurately categorizing expenses, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and present a transparent financial picture to potential lenders, strengthening the case for loan approval and fostering sustainable financial growth. This comprehensive view of expenditures allows lenders to assess risk and make informed lending decisions.
4. Profit Calculation
Profit calculation forms the core purpose of an SBA profit and loss statement template. The statement systematically organizes revenue and expense data to arrive at a net profit or loss figure. This calculation provides a crucial indicator of a business’s financial health and sustainability. A profitable business demonstrates its ability to generate revenue exceeding expenses, a key factor in securing SBA loans. For example, a business demonstrating consistent profitability over several reporting periods presents a stronger case for loan approval compared to one showing fluctuating or negative profit margins. The profit calculation provides quantifiable evidence of a business’s financial viability.
Several distinct profit calculations exist within the template, each offering unique insights. Gross profit, calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue, reveals the profitability of core business operations. Operating profit, derived by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, indicates the profitability of the business after accounting for day-to-day operational costs. Finally, net profit, the bottom line, represents the overall profitability after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been deducted. Analyzing these different profit figures provides a comprehensive understanding of a business’s financial performance at various levels. For instance, a declining gross profit margin could signal issues with production costs or pricing strategies, while a shrinking operating profit margin might indicate escalating overhead expenses. This granular analysis allows for targeted interventions and informed decision-making.
Understanding the nuances of profit calculation within the context of an SBA profit and loss statement is essential for both business owners and lenders. For business owners, it allows for performance evaluation, identification of areas for improvement, and informed strategic planning. For lenders, accurate profit calculation provides critical data for assessing creditworthiness and making sound lending decisions. Challenges can arise from inaccurate revenue or expense reporting, impacting the reliability of the profit calculation and potentially leading to flawed financial assessments. Therefore, maintaining accurate records and adhering to consistent accounting practices are crucial for generating reliable profit figures and presenting a clear financial picture. This ultimately facilitates access to capital and supports sustainable business growth.
5. Time Period Specification
Time period specification is integral to the SBA profit and loss statement template, providing the temporal context for financial performance analysis. Defining a specific timeframe, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, allows for accurate tracking of revenue and expenses within that period. This defined timeframe enables meaningful comparisons of financial performance across different periods, facilitating trend analysis and informed decision-making. For example, specifying monthly periods allows for the identification of seasonal sales fluctuations, while annual periods provide a broader overview of yearly performance. Without a defined time period, the financial data lacks context and becomes significantly less useful for analysis and planning.
The choice of time period depends on the specific needs of the business and the requirements of the SBA loan application. Short-term loans might require monthly profit and loss statements to monitor performance closely, while long-term loans might necessitate annual statements for a broader financial overview. Comparing performance across consistent time periods allows for the identification of growth patterns, declining profitability, or unusual fluctuations. For instance, consistent revenue growth over several quarters demonstrates positive business trajectory, while consecutive periods of declining profit might indicate underlying operational issues. This analysis enables proactive adjustments to business strategies and financial management practices.
Accurate time period specification is crucial for both internal management and external reporting. Internally, it supports informed decision-making based on timely and relevant financial data. Externally, it provides lenders with a clear and consistent view of financial performance, enhancing transparency and building confidence in the business’s financial stability. Challenges can arise from inconsistent time periods or incorrect data entry, leading to flawed analysis and potentially misrepresenting the business’s financial health. Maintaining rigorous accounting practices and adhering to consistent reporting periods are essential for accurate and reliable financial analysis based on the SBA profit and loss statement template. This ensures data integrity and facilitates sound financial management, ultimately contributing to business success and access to necessary capital.
6. SBA Loan Applications
The SBA profit and loss statement template plays a critical role in SBA loan applications. Lenders require a clear understanding of an applicant’s financial health to assess risk and make informed lending decisions. The template provides a standardized format for presenting financial performance, enabling lenders to evaluate key metrics such as revenue, expenses, and profitability. A well-prepared statement demonstrates financial transparency and professionalism, increasing the likelihood of loan approval. Conversely, incomplete or inaccurate statements can raise red flags and jeopardize the application process. For example, a business demonstrating consistent profitability and healthy cash flow through its profit and loss statement significantly strengthens its application compared to one presenting inconsistent or negative earnings.
The specific requirements for profit and loss statements vary depending on the loan program and the lender. Some programs might require historical data covering several years, while others might focus on projected future performance. Applicants must carefully review the specific guidelines and ensure their statements comply with all requirements. Providing additional financial documentation, such as balance sheets and cash flow statements, alongside the profit and loss statement can further strengthen the application. For instance, a business seeking a large loan for expansion might need to provide detailed financial projections based on market analysis and growth strategies, demonstrating the potential return on investment and ability to repay the loan. This comprehensive financial picture enhances the lender’s understanding of the business’s financial viability.
Understanding the integral connection between the SBA loan application process and the profit and loss statement is crucial for securing funding. Accurate, complete, and well-presented financial information increases the likelihood of loan approval, enabling businesses to access the capital needed for growth and success. Challenges can arise from inadequate record-keeping practices or a lack of understanding of accounting principles, leading to inaccurate or incomplete statements. Seeking professional guidance from accountants or financial advisors can help ensure accurate reporting and improve the chances of securing SBA funding. This proactive approach to financial management demonstrates commitment and strengthens the overall loan application.
Key Components of an SBA Profit and Loss Statement Template
Essential components comprise a robust and informative SBA profit and loss statement template. These components provide a structured framework for conveying critical financial information to lenders and stakeholders. Understanding these elements is crucial for accurate reporting and informed financial decision-making.
1. Revenue: Accurate revenue reporting forms the foundation of the statement. This section details all income generated from business activities, including gross revenue, net revenue, and revenue streams. Precise revenue figures are essential for calculating profitability and demonstrating financial health.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This component is crucial for determining gross profit margins and assessing the efficiency of production processes.
3. Operating Expenses: Operating expenses encompass all costs incurred in running the day-to-day operations of the business. Categorizing these expenses, including rent, salaries, and marketing costs, provides insight into operational efficiency and potential cost-saving opportunities.
4. Gross Profit: Gross profit, calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, reveals the profitability of core business operations before accounting for operating expenses. This metric provides a key indicator of the business’s ability to generate profit from its primary activities.
5. Operating Profit: Operating profit, calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, indicates the profitability of the business after accounting for day-to-day operational costs. This metric provides insight into the efficiency and sustainability of core business operations.
6. Other Income and Expenses: This section accounts for income and expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, interest expense, and depreciation. Accurate reporting in this section is essential for a complete financial picture.
7. Net Profit/Loss: Net profit, often referred to as the “bottom line,” represents the overall profitability after all revenue and expenses have been accounted for. This key figure provides a concise summary of the business’s financial performance over the specified period.
8. Reporting Period: Clearly specifying the reporting period, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually, provides crucial context for the financial data. Consistent reporting periods enable trend analysis and comparison of performance across different timeframes. This component allows for meaningful insights into financial performance within a defined period.
These components work together to provide a comprehensive overview of a business’s financial performance. Accurate and detailed reporting within each component enables informed decision-making, strengthens loan applications, and supports sustainable financial growth. This structured framework facilitates transparency and allows stakeholders to assess the financial health and viability of the business.
How to Create an SBA Profit and Loss Statement
Creating an accurate and comprehensive profit and loss statement is crucial for any business, especially when seeking SBA funding. The following steps outline the process of developing a statement that meets SBA requirements and provides a clear picture of financial performance.
1. Choose a Reporting Period: Select a specific timeframe for the statement, such as a month, quarter, or year. Consistent reporting periods allow for accurate tracking of financial performance over time and facilitate comparisons across different periods. This defined timeframe provides context for the financial data presented.
2. Calculate Revenue: Accurately record all revenue generated during the chosen reporting period. This includes gross revenue from all sales before any deductions. Clearly distinguish between different revenue streams if applicable, such as product sales versus service revenue. Subtract any returns, allowances, and discounts to arrive at net revenue.
3. Determine Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Calculate the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit margins.
4. Itemize Operating Expenses: Detail all operating expenses incurred during the reporting period. This encompasses costs related to running the business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Categorize expenses appropriately for a clear understanding of resource allocation.
5. Calculate Gross Profit: Subtract COGS from net revenue to arrive at gross profit. This figure represents the profitability of core business operations before accounting for operating expenses.
6. Calculate Operating Profit: Subtract operating expenses from gross profit to determine operating profit. This metric reflects the profitability of the business after accounting for day-to-day operational costs.
7. Account for Other Income and Expenses: Include any other income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, interest expense, depreciation, and amortization. This ensures a comprehensive view of the business’s financial activities.
8. Calculate Net Profit/Loss: Subtract all expenses, including other income and expenses, from the total revenue to arrive at the net profit or loss. This bottom-line figure provides a clear indication of the business’s overall profitability during the reporting period.
9. Review and Verify: Thoroughly review the completed statement for accuracy and completeness. Ensure all figures are correctly calculated and all necessary information is included. Accurate reporting is crucial for sound financial management and securing SBA funding. Consider consulting with a financial professional to ensure accuracy and compliance with SBA requirements. A well-prepared statement demonstrates financial transparency and professionalism, increasing the likelihood of loan approval.
Accurate financial reporting is paramount for business success, particularly when seeking funding through the Small Business Administration. The SBA profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting financial data, enabling lenders to assess key performance indicators such as revenue, expenses, and profitability. Understanding and utilizing this template effectively is essential for securing SBA loans and demonstrating financial stability. Careful attention to detail, accurate data entry, and adherence to reporting guidelines are crucial for creating a comprehensive and reliable statement. This meticulous approach to financial reporting facilitates transparency, builds trust with lenders, and supports informed decision-making.
Mastery of the SBA profit and loss statement template empowers businesses to present a clear and compelling narrative of their financial health. This, in turn, increases access to crucial funding opportunities and supports sustainable growth. Effective financial management, underpinned by accurate and insightful reporting, is a cornerstone of long-term business success. Continued diligence in maintaining accurate financial records and adhering to best practices in financial reporting will position businesses for sustained growth and financial stability.


