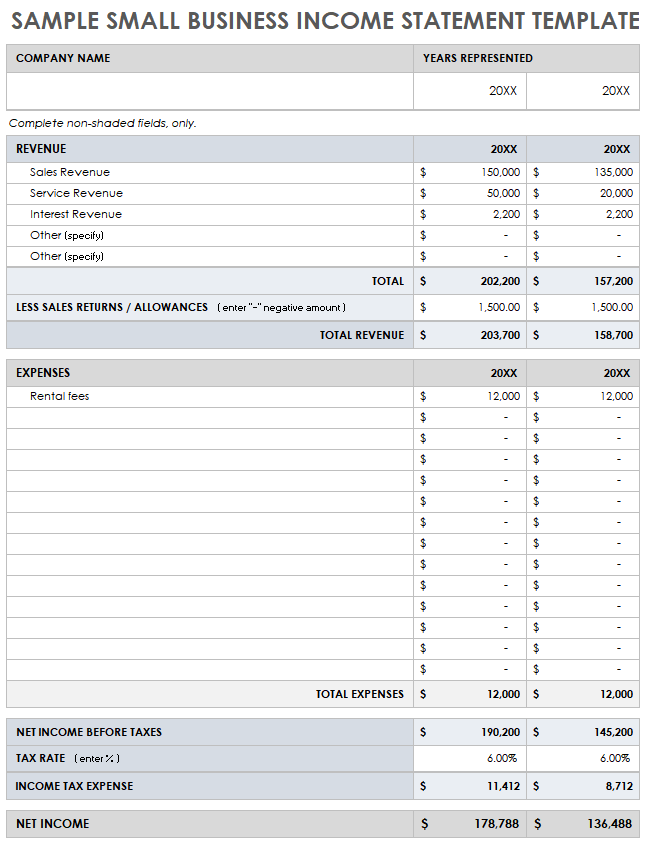
Utilizing a structured format for financial reporting offers several advantages. It promotes clarity and understanding of financial performance, supporting better decision-making. The consistent structure simplifies analysis and allows for efficient tracking of financial progress. This, in turn, can improve financial management and contribute to stronger financial health for businesses and individuals alike.

Understanding the structure and purpose of these reporting tools is fundamental to sound financial analysis. The following sections delve into the core components of these reports, offering practical guidance on their interpretation and application.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are crucial for simple financial statement templates. Consistency in structure and presentation allows for efficient data analysis and comparison. Standardization ensures reports are readily understandable across different users and periods, facilitating informed financial decision-making.
- Uniformity of PresentationUniformity ensures consistent placement of key financial elements. For example, assets are consistently listed on the left side of a balance sheet and revenues at the top of an income statement. This predictable structure enables quick identification of relevant information and streamlines comparative analysis across different reporting periods.
- Common TerminologyUtilizing standard financial terms ensures clarity and minimizes ambiguity. Terms such as “net income,” “current assets,” and “operating expenses” have specific, universally understood meanings. Consistent terminology facilitates communication and understanding among stakeholders, regardless of their accounting expertise.
- Comparable StructureA comparable structure enables benchmarking and trend analysis. Comparing a company’s performance against its historical data or industry averages requires consistent reporting formats. Standardized templates allow for meaningful comparison, revealing patterns and supporting informed decision-making.
- Simplified InterpretationA standardized format simplifies the interpretation of financial data. Users can readily understand the information presented without needing to decipher varying structures or terminology. This accessibility empowers stakeholders to extract meaningful insights and contribute to effective financial management.
These facets of standardization contribute to the overall effectiveness of simple financial statement templates. By promoting clarity, consistency, and comparability, standardized formats empower users to understand financial information effectively, facilitating sound financial analysis and informed decision-making.
2. Key Financial Elements
Effective financial statement templates hinge on the inclusion of key financial elements. These elements provide a comprehensive snapshot of an entity’s financial health and performance. A balance sheet, for instance, must include assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets represent what the entity owns, liabilities represent what it owes, and equity represents the owners’ stake. The relationship between these elements is fundamental to understanding financial position. An income statement, on the other hand, focuses on revenues and expenses over a specific period. The difference between these two elements reveals the entity’s profitability, a critical indicator of financial performance. Cash flow statements track cash inflows and outflows, categorized by operating, investing, and financing activities. This provides insights into liquidity and how the entity generates and uses cash.
Consider a retail business. Its balance sheet might show inventory as a significant asset, while rent represents a significant liability. The income statement would reflect sales revenue and cost of goods sold. The cash flow statement would show cash inflows from customer purchases and outflows for inventory purchases and operating expenses. Without these key elements, a comprehensive understanding of the business’s financial performance would be impossible. For instance, a large inventory balance without corresponding sales revenue could indicate overstocking and potential losses. Strong sales revenue coupled with negative cash flow from operations might signal difficulties with collections. The interplay of these elements provides valuable insights into the business’s health and potential risks.
Accurate and comprehensive inclusion of key financial elements is therefore essential for any financial statement template. Omitting or misrepresenting these elements can lead to misinformed decisions and hinder effective financial management. Understanding the relationships between these elements enables stakeholders to assess financial health, identify trends, and make sound decisions. This underscores the importance of well-designed templates that prioritize the clear and accurate presentation of key financial data.
3. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis is integral to the utility of simple financial statement templates. These templates facilitate the comparison of financial data across different periods or against industry benchmarks. This comparative approach unlocks crucial insights into trends, performance changes, and potential areas for improvement. A simple income statement template, for example, allows for year-over-year profit comparison. This comparison can reveal whether profitability is increasing or decreasing, informing strategic decisions regarding pricing, cost control, or expansion. Similarly, comparing key ratios derived from a balance sheet template, such as the current ratio or debt-to-equity ratio, against industry averages can highlight areas of strength and weakness relative to competitors. For instance, a lower-than-average current ratio might indicate potential liquidity issues requiring attention.
The practical significance of comparative analysis within simple financial statement templates extends beyond internal performance evaluation. Investors and lenders frequently use these comparative analyses to assess the financial health and creditworthiness of businesses. Consistent reporting through standardized templates ensures that these external stakeholders can readily understand and compare financial information, facilitating investment decisions and access to capital. Furthermore, comparing performance against budget projections, enabled by consistent template usage, allows for timely identification of variances and corrective action. For example, if actual expenses consistently exceed budgeted amounts, management can investigate the causes and implement cost-saving measures.
Effective comparative analysis, therefore, relies heavily on the structured and standardized nature of simple financial statement templates. These templates provide the necessary framework for consistent data organization and presentation, making comparison across periods and against benchmarks possible. This capability empowers stakeholders to identify trends, assess performance, and make informed decisions based on reliable and comparable financial information. The inability to conduct meaningful comparisons would significantly limit the usefulness of financial statements and hinder effective financial management.
4. Accessibility
Accessibility in the context of simple financial statement templates refers to the ease with which users can understand and utilize the information presented. Clear, concise, and well-structured templates are essential for ensuring that financial data is readily interpretable by a range of stakeholders, regardless of their financial expertise. Accessible templates empower informed decision-making and promote effective financial management.
- Clarity of PresentationClarity is paramount. Information should be presented in a logical, easy-to-follow format, avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical complexities. Effective use of visual aids, such as charts and graphs, can further enhance understanding, particularly for complex data. A balance sheet, for example, benefits from clear labeling of asset, liability, and equity sections, facilitating quick comprehension of the company’s financial position.
- User-Friendly FormatTemplates should be designed with the end-user in mind. A simple, intuitive layout, consistent use of terminology, and clear instructions contribute to a user-friendly experience. A small business owner, for instance, should be able to easily input data into an income statement template and quickly understand the resulting profit or loss figures without requiring extensive accounting knowledge.
- Availability of InformationAccessibility also encompasses the availability of the template itself. Templates should be readily available to relevant stakeholders, whether through easily accessible software, online platforms, or other readily distributable formats. This ensures that those who need the information can access it promptly and efficiently, supporting timely decision-making. For example, providing cloud-based access to financial statements allows investors to review performance data remotely and conveniently.
- Adaptability to Different NeedsRecognizing that users may have diverse needs and levels of financial literacy is critical. Templates should ideally offer varying levels of detail or customization options. A simplified template might suffice for a small business owner tracking basic financial metrics, while a more detailed version could be necessary for investors performing in-depth financial analysis. Offering different template versions caters to these varying requirements, ensuring accessibility for a wider range of users. An example could be a simplified income statement template focusing solely on revenue and expenses, alongside a more detailed version incorporating cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other granular financial data.
These facets of accessibility are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of simple financial statement templates. By prioritizing clarity, user-friendliness, availability, and adaptability, these templates become powerful tools for promoting financial transparency and informed decision-making among a diverse range of stakeholders. Inaccessible templates, conversely, can hinder understanding, lead to misinterpretations, and ultimately undermine effective financial management.
5. Regular Updates
Maintaining up-to-date financial records is paramount for accurate and relevant decision-making. Regular updates are essential for a simple financial statement template to reflect the current financial state of an individual or organization. Frequency depends on the specific needs and context; a small business owner might update income statements monthly to monitor profitability, while a publicly traded company adheres to quarterly and annual reporting requirements. Without regular updates, financial statements become outdated, potentially leading to misinformed decisions based on stale data. For example, relying on an outdated balance sheet might misrepresent the current asset and liability position, potentially obscuring emerging liquidity issues.
The cause-and-effect relationship between regular updates and the efficacy of a simple financial statement template is direct. Regular updates provide a current snapshot of financial health, enabling timely identification of trends, potential risks, and opportunities. This, in turn, supports proactive financial management. Consider a scenario where a company experiences a sudden increase in customer returns. Regularly updated income statements would promptly reflect the declining revenue and potentially increased expenses associated with processing returns. This allows management to investigate the root cause, implement corrective actions, and mitigate potential losses. Conversely, infrequent updates might delay the identification of this issue, exacerbating the negative impact on profitability.
Regular updates form a cornerstone of any effective financial management strategy relying on simple financial statement templates. They ensure data accuracy and relevance, facilitating informed decision-making. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the ability to respond proactively to changing financial conditions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities. Failure to maintain current financial information through regular updates undermines the very purpose of these templates, potentially leading to flawed analysis and suboptimal financial outcomes. This reinforces the importance of incorporating regular updates as a fundamental component of any sound financial reporting process.
6. Concise Presentation
Concise presentation is a critical aspect of effective financial reporting, particularly within the framework of simple financial statement templates. Templates prioritize clarity and efficiency, ensuring that key information is readily accessible without overwhelming the user with unnecessary detail. A concisely presented financial statement facilitates rapid comprehension and supports efficient decision-making.
- Information PrioritizationEffective concise presentation requires careful prioritization of information. Focus should be placed on key financial elements that directly contribute to understanding the entity’s financial position and performance. Non-essential details should be omitted to avoid clutter and maintain clarity. For example, a simple income statement template would prioritize revenue, expenses, and net income, while excluding less critical details like individual office supply expenses.
- Visual ClarityVisual clarity enhances conciseness. Utilizing clear and consistent formatting, appropriate spacing, and logical grouping of information improves readability and comprehension. Effective use of tables and charts can further enhance visual clarity by presenting data in a readily digestible format. For instance, a balance sheet benefits from clearly delineated sections for assets, liabilities, and equity, promoting rapid understanding of the entity’s financial structure.
- Elimination of RedundancyConcise presentation avoids redundancy. Information should be presented only once, avoiding unnecessary repetition. Duplicated data not only clutters the statement but also increases the risk of errors and inconsistencies. For example, in a cash flow statement, individual transactions should be categorized appropriately (operating, investing, or financing), avoiding the need to list the same transaction multiple times.
- Targeted Detail LevelThe level of detail presented should align with the intended audience and purpose of the financial statement. A simple income statement for internal management use might include more detailed expense breakdowns than a summarized version presented to external investors. Tailoring the level of detail ensures relevance and avoids overwhelming users with unnecessary information. For instance, a board of directors reviewing a balance sheet may require details on individual asset categories, while a creditor might primarily focus on overall liquidity ratios.
Concise presentation within simple financial statement templates enhances usability and facilitates informed decision-making. By prioritizing key information, maintaining visual clarity, eliminating redundancy, and tailoring the level of detail, these templates empower stakeholders to efficiently grasp the entity’s financial position and make sound judgments. Overly detailed or poorly organized statements, conversely, can obscure crucial insights and hinder effective financial analysis.
Key Components of Simple Financial Statement Templates
Effective financial statement templates rely on several key components working in concert. These components ensure clarity, accuracy, and usability, enabling stakeholders to understand an entity’s financial position and performance. The following elements are crucial for well-designed templates:
1. Standardized Structure: A standardized structure ensures consistency and comparability across reporting periods. This involves uniform placement of key elements, consistent terminology, and a predictable format. Standardization allows for efficient analysis and benchmarking.
2. Key Financial Elements: Templates must incorporate essential financial data points. A balance sheet requires assets, liabilities, and equity. An income statement needs revenues and expenses. A cash flow statement tracks cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. These elements provide a comprehensive financial overview.
3. Comparative Data Presentation: Facilitating comparisons across different periods or against benchmarks is crucial. Templates should allow for year-over-year analysis, trend identification, and performance evaluation relative to industry averages or budget projections.
4. Accessibility and Clarity: Information must be presented clearly and concisely, avoiding jargon and technical complexities. Visual aids, such as charts and graphs, can enhance understanding. A user-friendly format and readily available access further promote usability.
5. Regular Updates: Financial data must be kept current. Regular updates ensure accuracy and relevance, allowing for timely identification of trends and informed decision-making. The frequency of updates depends on the specific needs and context.
6. Concise and Focused Information: Templates should prioritize essential information and avoid unnecessary detail. A concise presentation facilitates rapid comprehension and efficient analysis, supporting effective decision-making. Visual clarity and the elimination of redundancy further enhance conciseness.
These components are essential for effective financial statement templates. Their combined effect ensures that financial information is presented clearly, accurately, and efficiently, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and manage finances effectively.
How to Create Simple Financial Statement Templates
Creating effective financial statement templates requires careful consideration of several key factors. A well-structured template ensures clarity, accuracy, and facilitates informed financial analysis. The following steps outline the process:
1. Determine the Purpose and Scope: Define the specific purpose of the template. Is it for internal management reporting, external investor communication, or loan applications? The intended use dictates the level of detail and complexity required. A template for internal use might include detailed expense breakdowns, while a version for external stakeholders would focus on key performance indicators.
2. Select Key Financial Elements: Identify the essential financial elements to include based on the template’s purpose. A balance sheet template requires assets, liabilities, and equity. An income statement template necessitates revenue and expense categories. A cash flow statement tracks cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. Choose elements relevant to the target audience and the decision-making needs they serve. For a small business tracking profitability, a simplified income statement focusing on revenue and major expense categories might suffice.
3. Choose a Standardized Format: Adopt a consistent format for presenting information. Standardized templates enhance comparability across periods and against benchmarks. Ensure consistent placement of key elements and use standard financial terminology. Leverage existing template structures or established accounting principles where applicable. For example, adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) ensures consistency and comparability with other financial statements.
4. Design for Clarity and Accessibility: Prioritize clear and concise presentation. Avoid jargon and technical complexities. Use clear labels, logical groupings, and appropriate spacing to enhance readability. Consider incorporating visual aids such as charts and graphs to present complex data effectively. Ensure the template is readily accessible to intended users through appropriate software or platforms. A cloud-based spreadsheet, for instance, allows for easy access and collaboration amongst stakeholders.
5. Incorporate Comparative Analysis Features: Include features that facilitate comparisons across periods and against relevant benchmarks. This may involve incorporating columns for previous periods, budget figures, or industry averages. Enable calculations of key ratios and metrics for performance evaluation. Year-over-year comparisons in an income statement, for instance, reveal profitability trends, while a balance sheet’s debt-to-equity ratio compared against industry averages offers insights into financial leverage.
6. Establish a Regular Update Process: Determine the appropriate frequency for updating the template based on the context and user needs. Regular updates ensure data accuracy and relevance for timely decision-making. Establish a clear process for data entry and verification to maintain data integrity. Automated data feeds from accounting software, for example, can streamline the update process and reduce manual errors.
Creating well-designed financial statement templates involves careful planning and execution. By considering the intended purpose, selecting relevant financial elements, adopting a standardized format, prioritizing clarity and accessibility, incorporating comparative analysis features, and establishing a regular update process, one can develop effective tools that support informed financial analysis and decision-making.
Streamlined reporting formats for financial data provide a crucial foundation for sound financial management. From aiding in internal performance analysis to facilitating communication with external stakeholders, these structured templates offer a powerful tool for understanding financial position, performance, and trends. Standardization, clarity, accessibility, and regular updates are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these templates. By incorporating key financial elements and facilitating comparative analysis, these templates empower informed decision-making, contributing to greater financial stability and success.
Effective utilization of these tools represents a commitment to financial transparency and informed decision-making. As financial landscapes continue to evolve, leveraging the power of well-designed templates becomes increasingly critical for navigating complexities and achieving financial objectives. The ability to readily interpret and act upon financial data is paramount, and adopting these standardized frameworks is a significant step toward achieving that goal. Ultimately, the consistent application of these principles contributes to a more robust and informed approach to financial management, fostering greater stability and success.


