Maintaining organized payment records offers several advantages. It simplifies financial reporting, facilitates accurate bookkeeping, and strengthens internal controls against errors and fraud. Furthermore, a well-maintained payment record can be invaluable for tax purposes, audits, and dispute resolution. It provides verifiable proof of transactions and enables efficient retrieval of payment information when needed. This organized approach to financial management contributes to improved transparency and accountability.

This foundation of organized financial record-keeping leads to discussions of topics such as choosing the right software, best practices for data entry, and strategies for ensuring data security. Understanding the underlying principles of proper payment documentation is essential for effective financial management in any context.
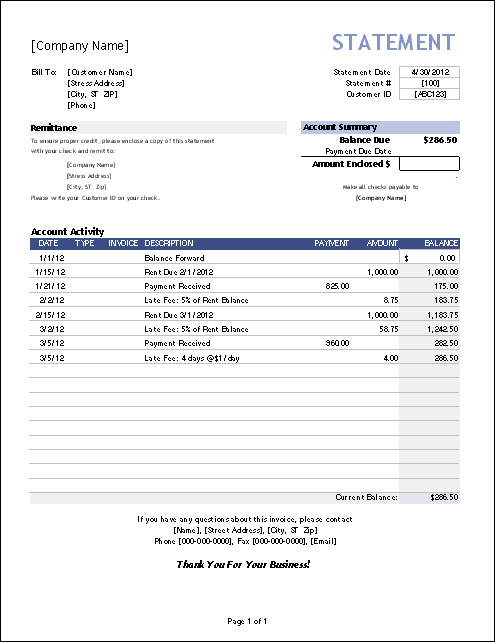
1. Standardized Format
Standardization is crucial for efficient payment processing and financial record-keeping. A standardized format within a payment record template ensures consistency and facilitates analysis. Consistent data entry allows for automated processing, streamlined reporting, and simplified reconciliation. This uniformity reduces errors caused by manual data entry variations and allows for easier comparison across different payments and periods. For example, a business processing numerous invoices benefits from a standardized template, ensuring each record contains identical fields for invoice number, date, amount, and client information, simplifying data sorting and analysis.
Standardization also promotes interoperability. Data from a standardized payment record can be easily integrated with other financial systems, such as accounting software or reporting tools. This interoperability streamlines workflows, eliminates redundant data entry, and improves overall financial management efficiency. Consider a scenario where a company needs to import payment data into its budgeting software. A standardized template ensures compatibility, eliminating the need for manual data manipulation and reducing the risk of errors.
In conclusion, a standardized format is essential for effective utilization of a payment record template. It improves data accuracy, facilitates analysis and reporting, and promotes seamless integration with other financial systems. While implementing standardized templates might require initial adjustments, the long-term benefits of streamlined processes and improved data integrity significantly outweigh the initial effort.
2. Payment Details
Comprehensive payment details form the core of any robust payment record. Within a standardized template, these details provide crucial information for accurate financial tracking and reconciliation. The inclusion of specific data points, such as payment date, amount, payer name, payment method (e.g., check, credit card, electronic transfer), and associated invoice or reference numbers, ensures clarity and traceability. Consider a business receiving multiple payments for various invoices. Without detailed information linking each payment to a specific invoice, reconciliation becomes complex and error-prone. Detailed records enable precise allocation of funds, minimizing discrepancies and facilitating accurate reporting.
The specificity of payment details directly impacts the effectiveness of financial analysis and decision-making. For instance, tracking payment methods can reveal trends in customer behavior or highlight potential processing fee discrepancies. Analyzing payment dates allows for accurate cash flow projections and informed resource allocation. Furthermore, detailed payment records are essential for audit trails, providing verifiable documentation for regulatory compliance and dispute resolution. In the event of a discrepancy, a detailed record allows for quick identification and resolution of the issue, minimizing financial losses and maintaining customer trust.
Accurate and comprehensive payment details are integral to a functional payment record template. This granular information empowers informed financial management, enabling effective tracking, analysis, and reporting. The absence of such detail undermines the integrity of financial records, increasing the risk of errors, hindering effective analysis, and potentially leading to compliance issues. Therefore, prioritizing the inclusion of comprehensive payment details within a standardized template is crucial for sound financial practices.
3. Record Keeping
Effective record keeping is inextricably linked to the utilization of a statement of payments received template. The template serves as a structured framework for organizing and storing payment information, ensuring data integrity and facilitating efficient retrieval. Without a systematic approach to record keeping, financial data becomes unwieldy, increasing the risk of errors, hindering analysis, and potentially leading to compliance issues. A well-maintained record, facilitated by the template, provides a clear audit trail, enabling traceability of transactions and supporting accountability. For example, a non-profit organization receiving donations from various sources benefits from a standardized template to track each contribution, ensuring accurate reporting for donors and regulatory bodies. This meticulous record keeping, facilitated by the template, builds trust and strengthens financial transparency.
The template’s structure reinforces consistent record keeping practices. Standardized fields within the template prompt the capture of essential payment details, minimizing omissions and ensuring uniformity across all records. This consistency simplifies data analysis, allowing for meaningful insights into financial trends and patterns. Consider a business analyzing its sales performance. A comprehensive payment record, organized through a template, enables detailed analysis of sales revenue by product, customer segment, or payment method, informing strategic decisions related to pricing, marketing, and inventory management. This analytical capability, enabled by consistent record keeping via the template, is crucial for informed business decision-making.
In summary, a statement of payments received template provides the essential structure for robust record keeping. This organized approach to financial data management promotes accuracy, facilitates analysis, and supports regulatory compliance. The template acts as a safeguard against data loss and disorganization, ensuring that financial information remains accessible, reliable, and readily available for informed decision-making. Challenges may arise in adapting to a structured template, particularly in organizations accustomed to less formal record-keeping practices. However, the long-term benefits of improved financial management, enhanced transparency, and reduced risk significantly outweigh the initial investment in implementing and maintaining a standardized system.
4. Financial Tracking
Financial tracking relies heavily on accurate and accessible data, a need directly addressed by a statement of payments received template. This template provides a structured framework for capturing comprehensive payment information, creating a foundation for robust financial analysis and informed decision-making. The template’s standardized format ensures consistent data entry, enabling automated processing and simplifying the generation of reports that provide insights into revenue streams, expense patterns, and overall financial health. For instance, a small business owner using the template to record all incoming payments can easily generate reports showing total revenue for a specific period, revenue by customer, or revenue by product, facilitating informed decisions regarding pricing, inventory, and resource allocation. Without this structured approach to data collection, financial tracking becomes cumbersome, increasing the risk of errors and hindering effective analysis.
The inherent connection between financial tracking and the template extends beyond basic data collection. The template’s structured format allows for the integration of payment data with other financial management tools, such as budgeting software or accounting platforms. This integration streamlines workflows, eliminates redundant data entry, and enhances the accuracy of financial projections. Consider a scenario where a project manager needs to track expenses against a budget. Utilizing a payment record template enables seamless integration of actual expenditure data with the project budget, providing real-time insights into project financial performance and facilitating proactive adjustments as needed. This integrated approach, facilitated by the template, strengthens financial control and improves project outcomes.
In conclusion, a statement of payments received template is instrumental for effective financial tracking. It provides the structure needed to collect, organize, and analyze payment data, enabling informed financial decision-making and supporting strategic planning. The template’s standardized format promotes accuracy, facilitates integration with other financial systems, and streamlines reporting processes. While implementing and maintaining a standardized template may require initial effort, the benefits of enhanced financial control, improved analytical capabilities, and informed decision-making far outweigh the initial investment. The template serves as a cornerstone of sound financial management practices, supporting organizations in achieving their financial objectives.
5. Audit Trails
A robust audit trail is a critical component of sound financial management, and a statement of payments received template plays a vital role in its creation. The template provides the structure for documenting every payment transaction, creating a chronological record that traces the flow of funds. This detailed record includes key information such as payment date, amount, payer, payment method, and associated invoice or reference numbers. This level of detail allows for the reconstruction of financial activities, facilitating the investigation of discrepancies, ensuring accountability, and supporting compliance with regulatory requirements. For example, in the event of a suspected fraudulent transaction, a comprehensive audit trail, constructed through consistent use of the template, allows investigators to trace the origin and destination of funds, identify irregularities, and gather evidence for potential legal action. Without such a detailed record, tracing financial activity becomes significantly more complex and potentially impossible.
The value of a well-maintained audit trail, facilitated by the consistent use of a payment received template, extends beyond reactive investigations. Proactive monitoring of payment records, enabled by the template’s structured format, allows organizations to identify potential issues before they escalate. Analyzing trends in payment methods, identifying unusual payment amounts, or detecting inconsistencies in payer information can reveal vulnerabilities in financial processes and highlight areas for improvement. For instance, a sudden increase in payments made via a specific method might trigger a review of processing fees or security protocols. This proactive approach to financial management, enabled by the structured data provided by the template, strengthens internal controls and mitigates financial risks.
In conclusion, a statement of payments received template is fundamental to establishing and maintaining a comprehensive audit trail. The template’s standardized format ensures the consistent capture of essential payment details, creating a chronological record of all transactions. This detailed record facilitates investigations, supports regulatory compliance, and enables proactive monitoring of financial activities. While the implementation of a standardized template may require initial effort, the long-term benefits of enhanced financial transparency, improved accountability, and reduced risk are undeniable. The template serves as a cornerstone of responsible financial management, providing the essential foundation for a robust audit trail that protects organizational assets and supports informed decision-making.
Key Components of a Payment Received Template
Essential data points within a standardized payment received template ensure comprehensive financial record-keeping. These components facilitate accurate tracking, analysis, and reporting of incoming payments.
1. Payment Date: The date the payment was received is fundamental for chronological tracking and reconciliation. Accurate date recording enables precise financial reporting and analysis of payment trends over specific periods.
2. Payer Information: Complete payer details, including name, address, and contact information, are essential for identifying the source of funds. This information is crucial for customer relationship management and facilitates efficient communication regarding payment inquiries.
3. Payment Amount: The precise amount received must be recorded accurately to maintain financial integrity. This data point is crucial for calculating total revenue, tracking outstanding balances, and generating accurate financial reports.
4. Payment Method: Documenting the payment method (e.g., cash, check, credit card, electronic transfer) provides valuable insights into payment trends and facilitates reconciliation with bank statements. This information can also be used to analyze transaction fees and optimize payment processing procedures.
5. Invoice or Reference Number: Linking each payment to a specific invoice or reference number is crucial for efficient reconciliation and accounts receivable management. This connection allows for clear tracking of outstanding invoices and facilitates prompt follow-up on overdue payments.
6. Description or Purpose of Payment: Including a brief description of the goods or services purchased or the purpose of the payment enhances clarity and facilitates future analysis of revenue streams. This detail is particularly valuable for businesses offering multiple products or services.
7. Received By: Recording the initials or name of the individual who processed the payment strengthens internal controls and accountability. This information is useful for tracking responsibility and resolving any discrepancies related to payment processing.
Accurate and comprehensive data capture within a standardized template ensures financial transparency, facilitates informed decision-making, and supports regulatory compliance. This structured approach to payment recording promotes efficient financial management and strengthens internal controls.
How to Create a Statement of Payments Received Template
Creating a standardized template ensures consistent and accurate recording of incoming payments. A well-designed template streamlines financial tracking, simplifies reporting, and strengthens internal controls. The following steps outline the process of creating an effective template.
1. Determine Required Information: Identify the essential data points needed to capture comprehensive payment information. Consider the specific requirements of the organization and relevant regulatory guidelines. Essential elements typically include payment date, payer information, amount, method, invoice/reference number, description, and received by.
2. Choose a Format: Select a format suitable for the intended use. Options include spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets), database software, or dedicated accounting software. The chosen format should allow for easy data entry, sorting, filtering, and report generation.
3. Create Column Headers: Clearly label each column with the corresponding data point. Consistent labeling ensures clarity and facilitates data analysis. Use concise and descriptive headers, such as “Payment Date,” “Payer Name,” “Amount,” “Payment Method,” “Invoice #,” “Description,” and “Received By.”
4. Format Cells for Data Entry: Format cells to accommodate the expected data type. For instance, format date columns for date values, currency columns for monetary values, and text columns for descriptive information. This formatting ensures data integrity and facilitates accurate calculations and analysis.
5. Incorporate Formulas for Calculations (Optional): If using spreadsheet software, incorporate formulas for automated calculations. For instance, calculate total payments received by summing individual payment amounts. Automated calculations improve accuracy and efficiency.
6. Test and Refine: Test the template with sample data to ensure functionality and identify potential issues. Refine the template based on testing results to optimize its effectiveness and usability. Ensure all formulas function correctly and data entry fields accommodate the necessary information.
7. Implement and Train: Implement the template within the organization and provide training to relevant personnel on its proper use. Consistent use of the template is essential for achieving data integrity and realizing the full benefits of standardized record-keeping. Clear instructions and practical examples should be included in training materials.
8. Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update the template to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Adapt the template to accommodate changes in business processes, regulatory requirements, or reporting needs. Periodic review and updates maintain the template’s relevance and effectiveness over time.
A standardized template facilitates consistent payment recording, improves financial tracking, simplifies reporting, and enhances internal controls. Consistent implementation and regular review ensure long-term effectiveness and adaptability.
Standardized documentation of incoming funds, facilitated by a dedicated template, forms a cornerstone of sound financial management. From accurate record-keeping and streamlined reporting to enhanced audit trails and informed decision-making, the benefits are substantial. Key components such as payment date, payer details, amount, method, and associated references ensure comprehensive data capture. Careful construction of such a template, including consideration of format, data fields, and potential integrations with other financial systems, is an investment in financial clarity and control. Consistent application and periodic review ensure the template’s ongoing effectiveness and adaptability to evolving organizational needs.
Effective financial management relies on accurate and accessible data. A well-implemented payment record template provides the structure necessary for achieving this objective. Organizations that prioritize the development and consistent use of these tools position themselves for financial stability, informed decision-making, and sustainable growth. The future of financial management lies in leveraging technology and standardized processes to enhance transparency, improve accountability, and drive informed decision-making. Embracing these principles is not merely a best practice but a necessity in today’s complex financial landscape.


