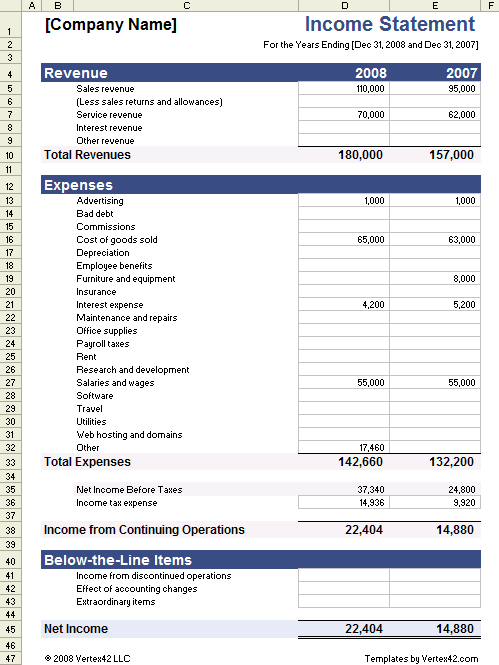
Utilizing a pre-structured form for financial reporting offers numerous advantages. It promotes consistency in reporting, simplifies the process of data entry and analysis, and reduces the likelihood of errors. This standardized approach facilitates comparisons across different accounting periods and allows for easier benchmarking against competitors or industry averages. Furthermore, it provides a readily available structure for budgeting and forecasting, which can be instrumental for strategic planning and decision-making.

This foundation of financial understanding allows for deeper exploration of related topics, such as interpreting key financial ratios derived from the data, strategies for revenue growth, and methods for controlling expenses. Understanding the structure and purpose of this form is crucial for informed financial analysis and effective business management.
1. Standardized Format
A standardized format is fundamental to the utility of a profit and loss template. Consistency in structure ensures data comparability across different periods and simplifies financial analysis. This standardization facilitates meaningful insights into an organization’s financial health and performance trends.
- Uniformity of CategoriesConsistent categorization of revenues and expenses is essential for accurate tracking and analysis. Uniform categories, such as “Revenue from Sales,” “Cost of Goods Sold,” “Operating Expenses,” and “Interest Expense,” allow for clear comparisons across reporting periods and facilitate the identification of trends. For example, consistent categorization of marketing expenses enables tracking of its effectiveness over time.
- Predefined CalculationsTemplates often include predefined calculations for key metrics like gross profit, operating income, and net income. These automated calculations minimize manual effort and reduce the risk of errors, ensuring accuracy and consistency in reporting. This automation allows for quicker analysis and decision-making.
- Structured LayoutA structured layout ensures information is presented clearly and logically. This typically involves a hierarchical presentation of revenues, followed by expenses, culminating in the net income or loss. A clear layout facilitates rapid comprehension and simplifies the process of extracting key insights from the data.
- Time Period ConsistencyStandardized templates typically specify the reporting period, whether it’s monthly, quarterly, or annually. Maintaining consistency in the reporting period is crucial for accurate trend analysis and performance evaluation. Comparing data from different timeframes can skew the interpretation of financial performance.
These elements of a standardized format contribute significantly to the value of a profit and loss template. By ensuring data consistency and clarity, the standardized format supports informed decision-making and contributes to effective financial management. Consistent application of these standards over time creates a reliable dataset for longitudinal analysis and strategic planning.
2. Financial Clarity
Financial clarity, a crucial outcome of a well-structured profit and loss statement, hinges on the organized presentation of revenue and expense data. A template provides the framework for this clarity, enabling stakeholders to understand the financial performance of an organization. Without a clear depiction of income and expenditures, assessing profitability and making informed decisions becomes significantly more challenging. For example, a business might experience strong sales but still struggle with profitability due to uncontrolled overhead costs. A profit and loss statement built on a sound template brings such discrepancies to light, allowing for timely intervention and corrective action.
The templates structure facilitates this clarity through categorized data. Clearly delineated sections for different revenue streams (e.g., product sales, service fees) and expense categories (e.g., salaries, rent, marketing) offer a granular view of financial activities. This detailed breakdown enables analysis of individual revenue and expense items, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of financial drivers. For instance, a retailer can analyze sales data by product line to identify top performers and underperforming items. This level of detail would be difficult to achieve without a structured approach to financial reporting.
In summary, a well-designed profit and loss template provides the foundation for financial clarity. This clarity empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate and readily accessible financial data. Challenges may arise in consistently applying the template and ensuring data accuracy, but the benefits of enhanced financial understanding significantly outweigh these potential obstacles. This clarity is not merely an organizational benefit; it also fosters trust and transparency with investors, lenders, and other external stakeholders, ultimately contributing to financial stability and growth.
3. Performance Tracking
Performance tracking relies heavily on the structured data provided by a statement of revenues and expenses template. This structured approach facilitates analysis of financial trends over time, enabling organizations to identify areas of strength and weakness. The template serves as a consistent framework for collecting and organizing financial data, making it possible to compare performance across different periods. Without this consistent structure, comparing financial results becomes significantly more challenging, hindering effective performance evaluation. For example, a business can track its gross profit margin over several quarters using data from its profit and loss statements, identifying trends and potential issues requiring further investigation. This consistent monitoring enables proactive management of profitability.
The insights gained through performance tracking, facilitated by the template, are crucial for informed decision-making. By analyzing trends in revenue and expenses, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement and potential risks. For instance, consistently increasing operating expenses as a percentage of revenue might signal inefficiency and prompt a review of cost structures. Similarly, declining sales in a specific product line, easily identified through categorized revenue data, can trigger targeted marketing campaigns or product revisions. These proactive measures, driven by performance tracking, are essential for long-term financial health and stability.
In conclusion, the statement of revenues and expenses template is an essential tool for effective performance tracking. The structured data it provides allows for consistent comparison and trend analysis, enabling organizations to identify areas for improvement and mitigate potential risks. While the template itself does not guarantee success, it provides the essential foundation for informed decision-making and proactive financial management. The challenge lies in accurately and consistently populating the template with reliable data, ensuring the resulting analysis is robust and actionable. This disciplined approach to financial record-keeping is fundamental to sound financial management.
4. Budgeting Foundation
A statement of revenues and expenses template serves as a crucial foundation for budgeting. Historical data captured within the template provides a realistic baseline for projecting future financial performance. By analyzing past revenue and expense trends, organizations can develop informed budgets that reflect anticipated market conditions and operational plans. Cause and effect relationships become clearer; for example, if historical data reveals a consistent correlation between marketing spend and sales growth, budget allocation for marketing can be strategically adjusted to achieve desired future sales targets. Without this historical context, budgeting becomes an exercise in guesswork rather than a strategic tool for financial management.
The templates structured format facilitates the budgeting process. Categorized revenue and expense data within the template translates directly into budget line items. This structure ensures comprehensive coverage of all revenue streams and expense categories, minimizing the risk of omissions and ensuring budgetary accuracy. Furthermore, the template promotes consistency between actual financial results and budgeted figures, simplifying variance analysis and performance evaluation. For example, a manufacturing company can use its prior year’s cost of goods sold, detailed within the template, as a starting point for budgeting production costs for the upcoming year, adjusting for anticipated changes in raw material prices or production volume. This methodical approach, grounded in historical data, strengthens budgetary control and enhances financial forecasting accuracy.
In summary, the statement of revenues and expenses template is indispensable for effective budgeting. It provides the historical context and structured framework necessary for developing realistic and achievable budgets. While the template itself does not guarantee budgetary success, it provides a critical foundation for informed financial planning and resource allocation. The key challenge lies in accurately interpreting historical trends and anticipating future market dynamics to create a budget that aligns with strategic objectives and promotes sustainable financial health. Overcoming this challenge requires a combination of rigorous data analysis, market understanding, and strategic foresight.
5. Informed Decisions
Informed financial decisions are predicated on a clear understanding of an organization’s financial performance. A statement of revenues and expenses template provides the structured data necessary for this understanding, enabling stakeholders to make strategic choices based on concrete evidence rather than conjecture. The template facilitates analysis of revenue streams, expense categories, and overall profitability, informing decisions related to pricing, cost control, investment strategies, and resource allocation. Without this structured data, decision-making processes become susceptible to biases and assumptions, increasing the risk of financial missteps.
- Strategic PricingUnderstanding the relationship between revenue and cost of goods sold, clearly delineated within the template, is crucial for setting profitable prices. Analysis of historical data can reveal the impact of price changes on sales volume and profitability, informing future pricing strategies. For instance, if data reveals that a small price increase has a negligible impact on sales volume, it might justify a strategic price adjustment to enhance profit margins.
- Cost OptimizationDetailed expense categorization within the template facilitates identification of areas where costs can be reduced without compromising operational efficiency or product quality. For example, analysis of historical data might reveal consistently increasing administrative expenses, prompting a review of administrative processes and potential cost-saving measures.
- Investment DecisionsEvaluating the profitability of different product lines or services, easily discernible through the template’s structured format, guides investment decisions. Resources can be allocated to high-performing areas with strong growth potential while underperforming areas may be restructured or divested. This data-driven approach optimizes resource allocation and maximizes return on investment.
- Resource AllocationUnderstanding the contribution of different departments or projects to overall profitability, facilitated by the template’s structure, informs resource allocation decisions. Departments or projects generating higher returns are likely to receive increased funding, while those with lower returns may face budget cuts or restructuring. This strategic allocation of resources maximizes organizational efficiency and supports growth objectives.
In conclusion, the statement of revenues and expenses template empowers informed decision-making by providing a clear and comprehensive view of financial performance. The insights derived from this structured data enable organizations to optimize pricing strategies, control costs, make strategic investments, and allocate resources effectively. The consistent application of this template over time creates a valuable repository of historical data, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of future decision-making processes. This data-driven approach to management is crucial for navigating complex market conditions and achieving sustainable financial success.
Key Components of a Statement of Revenues and Expenses Template
Effective financial analysis requires a structured approach to data organization. Key components within a statement of revenues and expenses template ensure comprehensive reporting and facilitate informed decision-making.
1. Revenue Streams: Clear identification of all revenue sources is essential. Categorization provides insights into the diverse contributors to overall income. Examples include sales revenue, service fees, and investment income. Disaggregating revenue allows for targeted analysis of each stream’s performance.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with production. Accurate COGS calculation is critical for determining gross profit and understanding product profitability. This typically includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
3. Operating Expenses: These expenses encompass the costs of running the business, excluding COGS. Categorization into selling, general, and administrative expenses allows for detailed analysis of operational efficiency. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing, and research and development.
4. Non-Operating Income and Expenses: These items represent income and expenses unrelated to core business operations. Examples include interest income, gains or losses from investments, and one-time charges. Proper classification ensures these items do not distort the analysis of operational performance.
5. Net Income/Loss: This bottom-line figure represents the overall profitability of the organization after all revenues and expenses are accounted for. It serves as a key indicator of financial health and sustainability. Trend analysis of net income over time provides crucial insights into long-term financial performance.
6. Reporting Period: Clearly defining the timeframe covered by the statement is essential for accurate comparison and analysis. Consistent reporting periods, whether monthly, quarterly, or annual, are crucial for tracking trends and identifying anomalies.
7. Supporting Documentation: Maintaining meticulous records supporting all revenue and expense figures ensures data accuracy and auditability. This documentation may include invoices, receipts, and bank statements. Reliable supporting data strengthens the credibility of the financial statement.
A comprehensive understanding of these components ensures accurate financial reporting and enables informed decision-making based on reliable data analysis. The structured format facilitates consistent tracking and analysis of financial performance, driving operational efficiency and strategic planning.
How to Create a Statement of Revenues and Expenses Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting. A well-structured template facilitates analysis, aids in budgeting, and supports informed decision-making. The following steps outline the process of template development.
1. Define Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the template. Common options include monthly, quarterly, or annually. Consistent reporting periods are crucial for comparability.
2. Establish Revenue Categories: Categorize revenue streams based on distinct sources. Examples include sales revenue, service fees, interest income, and other revenue. Detailed categorization facilitates analysis of individual revenue stream performance.
3. Outline Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, establish a clear structure for capturing COGS. Include direct material costs, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
4. Categorize Operating Expenses: Create distinct categories for operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing and advertising, research and development, and depreciation. Detailed categorization supports analysis of operational efficiency.
5. Include Non-Operating Income and Expenses: Incorporate sections for non-operating items, such as interest income, gains or losses from investments, and one-time charges. This ensures these items do not distort the analysis of core business operations.
6. Calculate Net Income/Loss: Include a formula to automatically calculate net income or loss by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. This bottom-line figure serves as a key indicator of overall profitability.
7. Incorporate Supporting Documentation Fields: Include fields for referencing supporting documentation, such as invoice numbers, receipt numbers, or other relevant identifiers. This enhances data integrity and facilitates audit trails.
8. Design for Clarity and Accessibility: Utilize a clear and logical layout for the template. Ensure data entry fields are clearly labeled and easy to navigate. A well-designed template enhances usability and minimizes data entry errors.
A well-designed template provides a framework for consistent data collection and analysis. This structure facilitates meaningful comparisons across reporting periods, enabling informed decision-making and supporting strategic financial management.
A standardized profit and loss structure provides a critical framework for understanding financial performance. From revenue streams and cost of goods sold to operating expenses and non-operating items, each component contributes to a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health. Utilizing a template ensures consistency in reporting, facilitates accurate trend analysis, and supports informed decision-making. The insights gleaned from this structured financial data are essential for effective budgeting, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate and accessible data. Adopting a standardized approach to profit and loss reporting, facilitated by a well-designed template, empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape. This structured approach provides a foundation for sustainable growth, informed by data-driven insights and proactive financial strategies. The consistent application of these principles is crucial for long-term financial stability and success.


