Utilizing a pre-designed structure for training initiatives offers several advantages. It promotes transparency by clearly articulating expectations and responsibilities. This clarity fosters accountability and streamlines communication between parties involved. Moreover, it aids in budget control by outlining anticipated costs and payment schedules. Finally, a well-defined plan facilitates a smoother training implementation process, ultimately increasing the likelihood of achieving desired learning outcomes.

The following sections will delve into the key components of this type of document, offering guidance on its creation and practical application. Topics will include defining learning objectives, outlining training methodologies, establishing assessment strategies, and managing contractual agreements. Practical examples and best practices will be provided to assist in developing comprehensive and effective training plans.
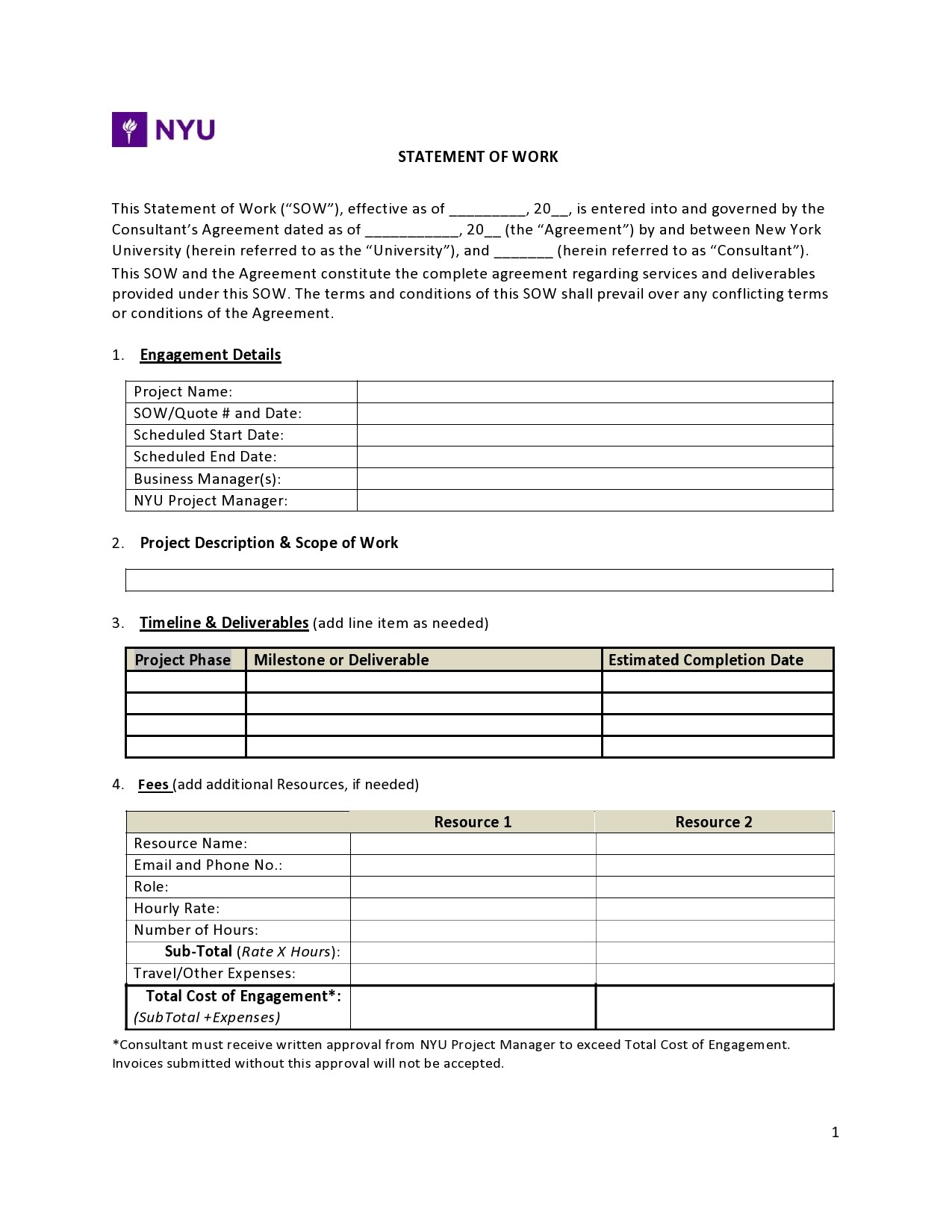
1. Scope Definition
Scope definition forms the bedrock of any effective training statement of work. A precisely defined scope ensures all stakeholders share a common understanding of the training initiative’s boundaries. This clarity prevents scope creep, where unanticipated tasks and requirements inflate the project beyond its original parameters. Scope definition encompasses several key elements: objectives, target audience, training content, delivery methods, and assessment criteria. For instance, a training program designed to enhance customer service skills for a call center team would have a different scope than a leadership development program for senior managers. The former might focus on specific communication techniques and problem-solving strategies, while the latter might concentrate on strategic thinking and change management.
Without a well-defined scope, a training initiative risks becoming unfocused and failing to meet its objectives. A vague or overly broad scope can lead to resource allocation issues, timeline overruns, and ultimately, ineffective training outcomes. Consider a scenario where a training program aims to improve employee productivity but lacks a clear definition of which specific skills or processes will be addressed. This ambiguity could result in a diluted curriculum that fails to deliver tangible improvements in employee performance. Conversely, a well-defined scope, outlining specific productivity-related skills and measurable performance metrics, provides a roadmap for achieving desired outcomes.
In conclusion, meticulous scope definition is essential for developing a robust training statement of work. It provides a framework for all subsequent planning and execution activities, ensuring alignment between the training initiative and organizational goals. Challenges in defining scope can arise from unclear stakeholder expectations or evolving business needs. Addressing these challenges proactively through thorough communication and ongoing review ensures the training program remains relevant and effective. A clear scope directly contributes to successful training outcomes, maximizing the return on investment and fostering organizational growth.
2. Deliverables
Clearly defined deliverables are essential components of a training statement of work template. They represent the tangible outputs or results expected upon completion of the training initiative. Specifying deliverables ensures all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the training’s intended outcomes. This clarity fosters accountability and allows for objective measurement of success. Deliverables can include various elements, such as training materials, participant workbooks, assessments, certifications, or software applications. A training program focused on software proficiency, for example, might list a certified user credential as a key deliverable. A leadership development program, on the other hand, might specify completion of a capstone project or presentation as a deliverable. The absence of clearly defined deliverables can lead to ambiguity and disputes regarding project completion and payment. Without concrete outputs, it becomes difficult to assess whether the training has achieved its objectives. This can result in dissatisfaction among stakeholders and undermine the effectiveness of the training investment.
The relationship between deliverables and the training statement of work template is one of cause and effect. Well-defined deliverables, documented within the template, drive the design and implementation of the training program. They serve as benchmarks against which progress is tracked and success is measured. Consider a sales training program. If a deliverable is an increase in sales conversions, the training content and methodology will be tailored towards achieving that specific outcome. The template would outline the metrics for measuring the increase and the timeframe for achieving it. In contrast, if the deliverable is the acquisition of a specific sales certification, the focus shifts towards exam preparation and successful completion. This demonstrates how deliverables influence the overall structure and content of the training program. Furthermore, clearly defined deliverables simplify the evaluation process. By establishing measurable outcomes upfront, stakeholders can assess the training’s effectiveness based on objective criteria.
In summary, deliverables function as critical components of a training statement of work template. They provide tangible targets, ensuring clarity of purpose, fostering accountability, and enabling effective evaluation. Challenges can arise when deliverables are poorly defined or unrealistic. Addressing these challenges requires careful consideration of organizational goals, available resources, and stakeholder expectations. A robust training statement of work, with clearly articulated deliverables, significantly contributes to the success of the training initiative and maximizes its impact on organizational performance.
3. Timeline
A well-defined timeline is a critical component of a training statement of work template. It provides a structured schedule for all training activities, from initial planning and development to implementation and evaluation. A realistic timeline ensures the training program progresses efficiently and concludes within the allocated timeframe. This temporal framework serves as a roadmap for all stakeholders, outlining key milestones and deadlines. A detailed timeline includes start and end dates for each phase of the training initiative, including content development, material preparation, delivery sessions, and assessments. For example, a six-month training program might allocate two months for curriculum development, three months for delivery, and one month for post-training evaluation and follow-up. Without a clear timeline, training initiatives risk delays, cost overruns, and ultimately, failure to achieve desired outcomes. A poorly planned timeline can lead to rushed development, inadequate preparation, and ineffective delivery. This can compromise the quality of the training and negatively impact participant learning.
The relationship between a timeline and a training statement of work template is one of structure and control. The timeline provides the temporal framework within which the scope of work, as defined in the template, is executed. It establishes a sequence of events and ensures that all activities are aligned with the overall training objectives. Consider a scenario where a company plans to launch a new product in the third quarter. The associated product training program, outlined in the statement of work, must be completed before the launch date. The timeline would dictate the start and end dates for curriculum development, trainer selection, participant enrollment, and training delivery, ensuring the training is completed in time to support the product launch. Conversely, a training program without a defined timeline risks missing critical deadlines, potentially delaying the product launch and impacting revenue. This illustrates the direct impact of the timeline on the success of the training initiative.
In conclusion, a well-defined timeline is indispensable for a successful training program. It provides structure, control, and predictability, ensuring all activities are aligned with project goals and deadlines. Challenges in timeline management can arise from unforeseen circumstances, such as resource constraints or changes in organizational priorities. Addressing these challenges requires proactive planning, ongoing monitoring, and flexible adaptation. A robust training statement of work template, incorporating a realistic and manageable timeline, significantly enhances the likelihood of achieving desired training outcomes and maximizing the return on investment.
4. Acceptance Criteria
Acceptance criteria within a training statement of work template define the specific conditions that must be met to deem the training initiative successfully completed. These criteria provide measurable standards for evaluating the training’s effectiveness and serve as a basis for formal acceptance by the client or stakeholder. Clear acceptance criteria ensure all parties share a common understanding of the expected outcomes, minimizing potential disputes and facilitating a smooth project conclusion. They transform abstract training objectives into concrete, verifiable results.
- Performance-Based Metrics:These criteria focus on demonstrable improvements in participant performance. Examples include achieving a specific score on a post-training assessment, demonstrating proficiency in a particular skill, or completing a project to a defined standard. A sales training program might specify a 15% increase in sales conversions as an acceptance criterion. This provides a quantifiable measure of training effectiveness tied directly to business outcomes.
- Completion Rates:These criteria track the percentage of participants who successfully complete the training program. A high completion rate often indicates effective program design and engagement. However, completion alone doesn’t guarantee skill acquisition or performance improvement. It’s crucial to combine completion rates with other performance-based metrics for a comprehensive evaluation. For instance, a mandatory compliance training program might require 100% completion, but additional criteria, such as a post-training assessment, would ensure comprehension and application of the learned material.
- Certification Requirements:For certain training programs, obtaining a specific certification serves as a key acceptance criterion. This applies to areas requiring standardized credentials, such as technical skills or professional certifications. Successful completion of a certification exam validates the training’s effectiveness in preparing participants for industry-recognized standards. A project management training program might require participants to obtain a Project Management Professional (PMP) certification as an acceptance criterion.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction:While often subjective, stakeholder satisfaction can serve as a valuable acceptance criterion. Feedback surveys and post-training evaluations can gauge participant satisfaction with the training content, delivery methods, and overall experience. Positive feedback contributes to program acceptance and future improvements. However, relying solely on subjective feedback might not accurately reflect the training’s impact on performance or organizational goals. Therefore, stakeholder satisfaction should be considered in conjunction with other, more objective criteria.
Clearly defined acceptance criteria within the training statement of work template are crucial for successful project completion. They provide a framework for evaluating the training’s effectiveness, ensuring alignment between training outcomes and organizational objectives. Ambiguity in acceptance criteria can lead to disputes and dissatisfaction. Therefore, meticulously defining these criteria upfront is essential for a successful training initiative. Well-defined acceptance criteria promote accountability, transparency, and ultimately, contribute to a positive return on investment for the training program.
5. Payment Schedule
A clearly defined payment schedule is an integral component of a training statement of work template. It outlines the financial agreement between the training provider and the client, specifying the total cost, payment milestones, and payment methods. This transparent financial framework ensures both parties understand their financial obligations, minimizing potential disputes and fostering a positive business relationship. A well-structured payment schedule aligns financial transactions with project milestones, providing a mechanism for tracking progress and ensuring timely compensation for delivered services. For example, a training program might specify a 20% upfront payment upon contract signing, 50% upon delivery of training materials, and the remaining 30% upon successful completion of the program as measured against the defined acceptance criteria. This structured approach links payments to deliverables, incentivizing timely performance and protecting the interests of both the client and the provider.
The payment schedule’s inclusion in the training statement of work template reinforces the document’s role as a comprehensive agreement governing all aspects of the training initiative. It establishes a direct link between financial commitments and project deliverables, ensuring accountability and transparency. Consider a scenario where a training program requires the development of customized training materials. The payment schedule might tie a portion of the payment to the delivery of these materials. This motivates the training provider to deliver the materials on time and to the agreed-upon specifications. Conversely, if the payment schedule is vague or incomplete, it can lead to delays in payments, strained relationships, and potential project disruptions. This underscores the importance of a well-defined payment schedule in ensuring smooth project execution.
In conclusion, a comprehensive payment schedule contributes significantly to the effectiveness of a training statement of work template. It fosters financial transparency, protects the interests of all parties involved, and promotes timely project completion. Challenges can arise when payment schedules are not aligned with project milestones or when unforeseen circumstances necessitate adjustments to the agreed-upon terms. Addressing these challenges requires proactive communication, flexibility, and a willingness to negotiate mutually acceptable solutions. A robust training statement of work, incorporating a clear and comprehensive payment schedule, strengthens the contractual agreement and contributes to a successful training initiative.
Key Components of a Training Statement of Work Template
A comprehensive training statement of work template requires several key components to ensure clarity, manage expectations, and facilitate successful project completion. These components provide a structured framework for outlining the training initiative’s scope, deliverables, timeline, and financial arrangements.
1. Introduction/Project Overview: This section provides a concise overview of the training program, its purpose, and intended outcomes. It sets the context for the entire document and establishes a shared understanding of the training initiative’s goals.
2. Scope of Work: This component details the specific training activities included in the project. It defines the boundaries of the training initiative, outlining what is included and, importantly, what is excluded. This clarity prevents scope creep and ensures all stakeholders are aligned on the project’s parameters.
3. Deliverables: This section lists the tangible outputs expected upon completion of the training program. Examples include training materials, assessments, certifications, or software applications. Clearly defined deliverables facilitate objective measurement of project success.
4. Timeline: A detailed timeline outlines the schedule for all training activities, including key milestones and deadlines. This provides a structured framework for managing the project and ensuring timely completion.
5. Acceptance Criteria: This component specifies the conditions that must be met to deem the training successfully completed. These criteria provide measurable standards for evaluating the training’s effectiveness and serve as a basis for formal acceptance.
6. Payment Schedule: This section outlines the financial agreement between the training provider and the client. It specifies the total cost, payment milestones, and payment methods, ensuring transparency and facilitating timely compensation for delivered services.
7. Training Resources & Logistics: This clarifies necessary resources like training venue, equipment, software, and the responsibilities for securing them. It addresses logistical aspects like catering, accommodation if needed, and technical support. This ensures a smooth and efficient training execution.
8. Project Governance: This section designates key personnel responsible for managing the training project and making decisions. It outlines communication channels and reporting procedures. This ensures proper oversight and accountability throughout the training lifecycle.
A well-defined training statement of work template, encompassing these key components, provides a solid foundation for successful training initiatives. This structure ensures clarity, manages expectations, and fosters a collaborative partnership between the training provider and the client, ultimately contributing to achieving desired learning outcomes and maximizing the return on investment.
How to Create a Training Statement of Work Template
Creating a robust training statement of work template requires a structured approach and careful consideration of key components. A well-defined template ensures clarity, manages expectations, and facilitates a successful training initiative.
1. Define Training Objectives: Clearly articulate the desired learning outcomes and how they align with organizational goals. Specificity is crucial. Ambiguous objectives lead to ineffective training programs. Measurable objectives enable accurate evaluation of training effectiveness.
2. Outline Scope of Work: Detail the specific training activities included in the project. Define boundaries, specifying what is included and excluded. This prevents scope creep and ensures all stakeholders understand the project parameters. Consider potential challenges and develop mitigation strategies.
3. Specify Deliverables: List tangible outputs expected upon completion. Examples include training materials, assessments, certifications, or software applications. Clearly defined deliverables enable objective measurement of project success. Link deliverables directly to training objectives.
4. Establish a Timeline: Develop a realistic schedule for all training activities, including key milestones and deadlines. A well-defined timeline ensures timely completion and efficient resource allocation. Account for potential delays and incorporate buffer time.
5. Define Acceptance Criteria: Specify conditions for successful completion. These criteria provide measurable standards for evaluating training effectiveness and serve as a basis for formal acceptance. Tie acceptance criteria to defined deliverables and objectives.
6. Develop a Payment Schedule: Outline the financial agreement, specifying total cost, payment milestones, and methods. A transparent payment schedule minimizes financial disputes and fosters a positive business relationship. Link payments to deliverables and milestones.
7. Outline Training Resources and Logistics: Specify necessary resources such as venue, equipment, and software. Clarify responsibilities for securing resources. Address logistical aspects like catering, accommodation (if needed), and technical support. Thorough planning ensures smooth training execution.
8. Establish Project Governance: Designate key personnel responsible for managing the training project and decision-making. Outline communication channels and reporting procedures. Effective governance ensures accountability and facilitates timely issue resolution.
A comprehensive training statement of work template, incorporating these elements, establishes a solid foundation for a successful training initiative. This structured approach promotes clarity, manages expectations, and fosters a collaborative partnership between the training provider and the client, ultimately contributing to the achievement of desired learning outcomes and a positive return on investment.
Careful planning and meticulous documentation are essential for effective training initiatives. A training statement of work template provides a structured framework for defining the scope of training programs, outlining deliverables, establishing timelines, and clarifying financial arrangements. This formalized approach ensures clarity, manages expectations, and minimizes potential misunderstandings between training providers and clients. By incorporating key components such as clear objectives, measurable deliverables, realistic timelines, and well-defined acceptance criteria, organizations can maximize the impact of their training investments and achieve desired learning outcomes. A comprehensive training statement of work template serves as a critical tool for managing training projects effectively, fostering accountability, and ensuring successful implementation.
Effective training programs are crucial for organizational success in today’s dynamic environment. Investing in well-structured training initiatives, guided by a comprehensive statement of work, empowers organizations to develop a skilled and adaptable workforce. This proactive approach enhances employee performance, drives innovation, and strengthens competitive advantage. Organizations that prioritize structured training programs, underpinned by robust documentation, position themselves for long-term success and adaptability in the face of evolving industry demands.


