Regularly generated cumulative reports allow for ongoing performance monitoring, enabling timely identification of trends and potential issues. This allows for proactive adjustments to strategies and operations throughout the year. These reports are also crucial for informing key stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and management, about current financial standing and progress towards established goals.

Further exploration will delve into the specific components of these reports, different available formats, and best practices for generating and interpreting this essential financial tool. This includes discussing various software solutions and considering the specific reporting needs of diverse organizational structures.
1. Cumulative Performance
Cumulative performance, a core element of year-to-date financial statements, provides a holistic view of an organization’s financial activities from the beginning of the fiscal year to a specific reporting date. This ongoing aggregation of financial data offers valuable insights into trends, progress, and potential areas for improvement, unlike isolated snapshots of performance.
- Revenue StreamsCumulative revenue tracking reveals patterns in sales and income generation over time. For example, a seasonal business can analyze year-to-date revenue to understand peak periods and lulls, informing inventory management and marketing strategies. This data is crucial for projecting annual revenue and making informed decisions about resource allocation.
- Expense ManagementMonitoring cumulative expenses provides a clear picture of spending patterns and cost control effectiveness. Tracking expenses against budget allows for proactive adjustments and prevents overspending. For instance, a company noticing a consistent rise in operational costs can investigate the cause and implement cost-saving measures.
- Profitability AnalysisAnalyzing cumulative profit, derived from the difference between cumulative revenues and expenses, offers insights into overall financial health and the effectiveness of business strategies. Tracking profit margins throughout the year helps identify factors impacting profitability and allows for timely adjustments to pricing, production, or operational strategies.
- Cash Flow MonitoringCumulative cash flow reflects the net movement of cash in and out of the organization. This ongoing tracking helps assess liquidity, predict potential cash shortages, and manage working capital effectively. Consistent monitoring of cash flow can alert management to the need for financing or adjustments to payment terms.
By integrating these facets of cumulative performance, year-to-date financial statements provide a comprehensive narrative of an organization’s financial trajectory throughout the year. This dynamic view enables informed decision-making, proactive adjustments, and effective communication with stakeholders regarding financial progress and stability.
2. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are fundamental to year-to-date financial statement templates. Consistency in presentation ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and performance evaluation. A structured format also simplifies data interpretation for stakeholders, promoting transparency and understanding. Specific elements within a standardized template typically include clearly defined sections for revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. Uniformity in these sections allows for straightforward comparison of financial data month-over-month or year-over-year. For example, a standardized income statement consistently presents revenue figures at the top, followed by cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income. This predictable structure enables stakeholders to quickly locate and interpret key performance indicators.
The use of standardized templates contributes to efficient data aggregation and analysis. Software applications designed for financial reporting often rely on standardized data input formats. This compatibility streamlines the process of generating reports and performing calculations. Consider a business utilizing a standardized template for tracking sales data. This data can then be seamlessly imported into accounting software to generate year-to-date reports, calculate sales tax liabilities, or analyze sales trends by product category. Furthermore, standardized formats are often required for regulatory reporting and compliance. Consistent reporting structures ensure organizations meet legal requirements and provide comparable financial information to regulatory bodies.
In conclusion, adherence to standardized formats in year-to-date financial statements enhances data comparability, simplifies interpretation, and facilitates integration with reporting tools. This structured approach fosters transparency, supports informed decision-making, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. While specific reporting requirements may vary by industry or organizational structure, the underlying principle of standardized presentation remains crucial for effective financial reporting and analysis.
3. Regular Updates
Regular updates are essential for maximizing the utility of year-to-date financial statement templates. The frequency of updates directly impacts the accuracy and relevance of financial insights derived from these reports. Timely updates ensure that decisions are based on current data, enabling proactive responses to changing financial conditions. For example, a monthly update cycle allows businesses to monitor cash flow trends and identify potential shortfalls early, enabling timely interventions such as adjusting expenditure or securing short-term financing.
The cadence of updates should align with the specific needs and dynamics of the organization. A rapidly growing startup might require more frequent updates, perhaps weekly or bi-weekly, to track key performance indicators and inform rapid strategic adjustments. A more established, stable organization might find monthly or quarterly updates sufficient for monitoring performance and maintaining stakeholder awareness. Irrespective of the chosen frequency, maintaining consistent updates is crucial for establishing reliable performance benchmarks and tracking progress against established targets. Consider a retail business tracking sales performance. Regular updates to the year-to-date sales figures provide insights into seasonal trends, the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, and the performance of individual product lines. This data informs inventory management decisions, pricing strategies, and future marketing initiatives.
Consistent updates also contribute to greater transparency and accountability. Regularly sharing updated financial information with stakeholders fosters trust and demonstrates a commitment to open communication. This is particularly important for investors, lenders, and regulatory bodies who rely on accurate and up-to-date financial information to assess risk and make informed decisions. Furthermore, a disciplined approach to regular updates reinforces sound financial management practices. It encourages ongoing monitoring and analysis, promoting proactive identification of potential challenges and opportunities. Ultimately, regular updates are integral to leveraging the full potential of year-to-date financial statement templates, enabling informed decision-making, promoting transparency, and supporting effective financial management.
4. Informed Decisions
Informed decisions represent the culmination of utilizing year-to-date financial statement templates. These templates provide the crucial data foundation upon which strategic choices are built. The comprehensiveness of year-to-date data, encompassing financial activity from the fiscal year’s beginning to the present, offers a significant advantage over isolated snapshots of financial performance. This cumulative perspective allows for the identification of trends, the assessment of progress towards goals, and the recognition of potential challenges or opportunities. Consider a manufacturing company analyzing its year-to-date production costs. Rising material costs, identified through consistent tracking, might prompt a decision to explore alternative suppliers or adjust product pricing. Conversely, a positive trend in sales revenue, observed through year-to-date figures, might justify investment in increased production capacity or expansion into new markets.
The ability to make informed decisions based on year-to-date data is paramount for effective resource allocation. Understanding revenue streams, expense patterns, and profitability trends allows organizations to allocate resources efficiently and maximize returns. For example, a non-profit organization tracking year-to-date donations can identify which fundraising campaigns are most successful and allocate future resources accordingly. Similarly, a retail business analyzing year-to-date sales data can identify underperforming product lines and reallocate shelf space or marketing efforts to more profitable items. The timeliness of data provided by regularly updated year-to-date reports is equally crucial. Prompt access to current financial information enables agile responses to changing market conditions and mitigates potential risks. A business experiencing a sudden downturn in sales, revealed by its latest year-to-date figures, can quickly implement cost-saving measures or adjust its marketing strategy to counter the decline.
In summary, informed decisions are the ultimate outcome of effectively utilizing year-to-date financial statement templates. The depth of insight provided by cumulative data, combined with the timeliness of regular updates, empowers organizations to allocate resources strategically, respond proactively to market dynamics, and navigate challenges with informed and calculated choices. The ability to leverage these insights represents a significant competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business environment, enabling organizations to adapt, innovate, and achieve sustainable growth.
5. Stakeholder Communication
Effective stakeholder communication is intrinsically linked to the utilization of year-to-date financial statement templates. These templates serve as a crucial tool for conveying financial performance and progress to various stakeholders, fostering transparency and informed decision-making. Clear, concise, and readily interpretable financial data, presented through these templates, strengthens relationships with investors, lenders, regulatory bodies, and internal management teams. Regularly updated year-to-date reports provide a consistent flow of information, ensuring stakeholders remain informed about the organization’s financial health and trajectory.
- Investor RelationsYear-to-date financial statements provide investors with essential insights into an organization’s financial performance. These reports demonstrate how invested capital is being utilized and the returns generated. Consistent reporting builds trust and allows investors to assess the organization’s progress towards stated goals. For example, a startup presenting strong year-to-date revenue growth can attract further investment or secure more favorable terms from existing investors. Conversely, transparent reporting of financial challenges can facilitate constructive dialogue and collaborative problem-solving with investors.
- Lender ConfidenceFinancial institutions rely on year-to-date statements to assess creditworthiness and monitor loan compliance. These reports provide evidence of an organization’s ability to manage finances and generate sufficient cash flow to meet debt obligations. Regularly updated year-to-date data strengthens lender confidence and supports access to favorable financing terms. A business demonstrating consistent profitability and healthy cash flow through its year-to-date statements is more likely to secure loans at competitive interest rates. Conversely, proactive disclosure of financial difficulties through these reports can facilitate early intervention and collaborative solutions with lenders.
- Regulatory ComplianceMany regulatory bodies require organizations to submit periodic financial reports, often based on year-to-date figures. These reports ensure compliance with industry regulations and provide transparency to the public. Accurate and timely submission of year-to-date financial statements demonstrates adherence to legal requirements and fosters public trust. For example, publicly traded companies are required to file quarterly reports with securities regulators, often incorporating year-to-date financial data. Consistent compliance builds credibility and avoids potential penalties.
- Internal ManagementYear-to-date financial statements are essential tools for internal management teams. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making regarding resource allocation, budgeting, and strategic planning. Regularly reviewing year-to-date figures allows management to identify trends, track progress towards key performance indicators, and make necessary adjustments to operations or strategies. For instance, a sales team can use year-to-date sales figures to evaluate the effectiveness of different sales strategies or identify top-performing regions. This data-driven approach empowers management to make informed decisions that drive organizational success.
In conclusion, year-to-date financial statement templates serve as a cornerstone of effective stakeholder communication. By providing a clear, consistent, and readily accessible view of financial performance, these reports foster transparency, build trust, and support informed decision-making across all stakeholder groups. This open communication contributes to stronger relationships, enhanced credibility, and ultimately, the long-term success of the organization.
Key Components of a Year-to-Date Financial Statement Template
Effective financial reporting hinges on well-structured documents. Key components within a year-to-date financial statement template ensure comprehensive data capture and facilitate informed analysis.
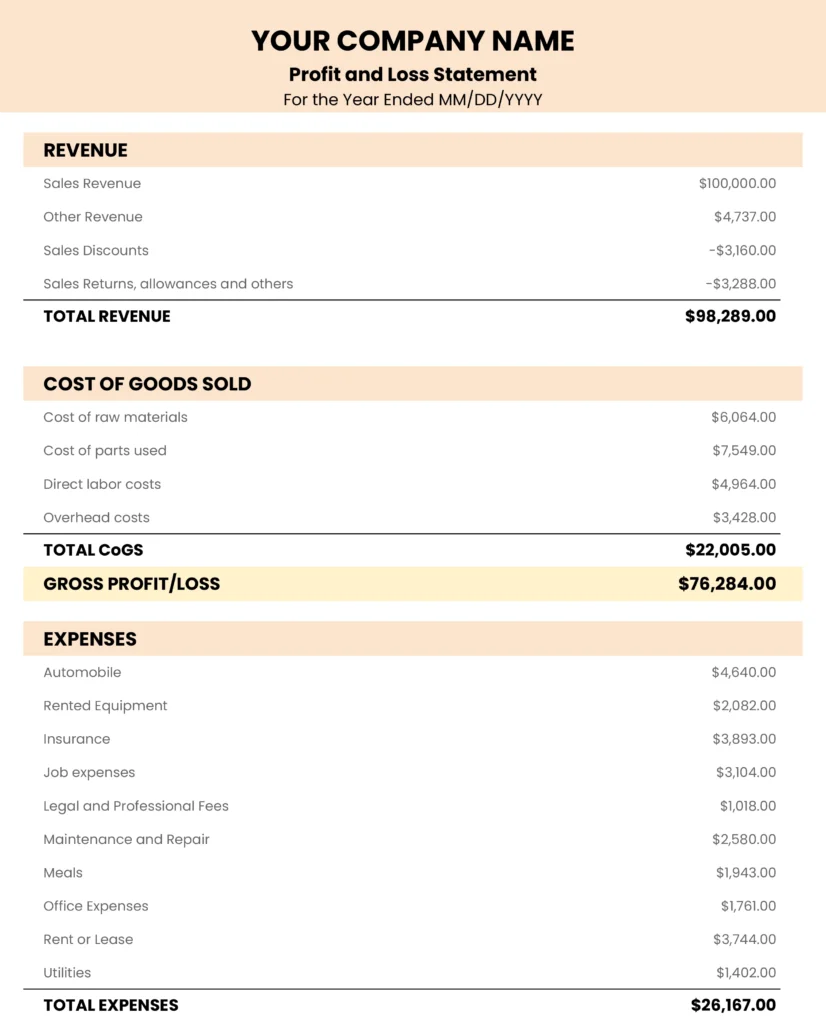
1. Income Statement Data: This section captures revenue generated, cost of goods sold (if applicable), and operating expenses. Gross profit, operating income, and net income are derived from these figures, providing insight into profitability.
2. Balance Sheet Data: A snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity at the reporting date offers a concise view of financial position. This section details current and long-term assets, current and long-term liabilities, and the resulting equity position.
3. Cash Flow Statement Data: This component tracks cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. Understanding cash flow dynamics is crucial for assessing liquidity and short-term financial stability.
4. Statement of Changes in Equity: This statement details changes in equity over the reporting period, including retained earnings, additional investments, and distributions. It provides insights into how equity has changed over time.
5. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): While not a formal statement, incorporating relevant KPIs enhances the analytical value of the template. Examples include gross profit margin, net profit margin, current ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio. Selecting KPIs relevant to the specific industry or organization enhances data interpretation.
6. Reporting Date: Clearly indicating the specific date up to which the financial data is compiled is essential for accurate interpretation and comparability. This allows stakeholders to understand the timeframe covered by the report.
7. Year-to-Date Comparison: Presenting data alongside figures from the same period in the previous year provides valuable context for evaluating performance trends and growth. This comparison facilitates identification of areas of improvement or concern.
These components work together to create a comprehensive overview of financial performance, supporting strategic decision-making and stakeholder communication.
How to Create a Year-to-Date Financial Statement Template
Creating a robust year-to-date financial statement template requires careful consideration of key data points and a structured approach. The following steps outline the process:
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the precise start and end dates for the report. This ensures clarity and allows for accurate comparisons across periods. For example, a year-to-date report for the third quarter would cover January 1st to September 30th.
2. Choose Relevant Financial Statements: Determine which statements are necessary to provide a comprehensive overview of performance. Common choices include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. The specific requirements may vary based on the organization’s size and industry.
3. Select Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify the most relevant KPIs for tracking progress and performance. Examples include gross profit margin, net profit margin, return on assets, and current ratio. Choose KPIs that align with organizational goals and industry benchmarks.
4. Design the Template Structure: Organize the template logically, with clear sections for each financial statement and KPI. Ensure consistent formatting for readability and comparability. Consider using a tabular format for easy data entry and analysis.
5. Incorporate Formulas and Calculations: Embed formulas within the template to automate calculations. This minimizes manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors. For example, formulas can automatically calculate gross profit, net income, or ratios based on inputted data.
6. Implement Data Validation: Include data validation rules within the template to ensure data accuracy and consistency. This prevents incorrect data entry and maintains the integrity of the financial information. For example, validation rules can restrict data entry to specific number formats or ranges.
7. Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the template with sample data to verify accuracy and functionality. Identify any errors or inconsistencies and make necessary adjustments. Regular review and refinement ensure the template remains relevant and effective.
8. Document the Template: Provide clear instructions and explanations for using the template. This ensures consistent application and facilitates interpretation of the reported data. Documentation should include definitions of KPIs and explanations of formulas used.
A well-designed template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting, supporting informed decision-making and effective communication with stakeholders.
Accurate and timely financial information is the bedrock of sound decision-making in any organization. Year-to-date financial statement templates provide a crucial framework for capturing, analyzing, and communicating this information effectively. From cumulative performance analysis and standardized reporting to regular updates and informed decisions, these templates empower organizations to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape. Understanding the key components, creation process, and strategic utilization of these templates is essential for maintaining financial health, promoting transparency, and achieving sustained growth.
Leveraging the power of year-to-date financial data enables organizations to not only react to current financial conditions but also to anticipate future trends and proactively shape their financial trajectory. This forward-looking perspective, supported by robust data analysis, is paramount in today’s dynamic business environment, offering a competitive edge and fostering long-term sustainability. Embracing a disciplined approach to financial reporting through well-structured templates equips organizations with the insights needed to thrive in the face of evolving challenges and opportunities.


