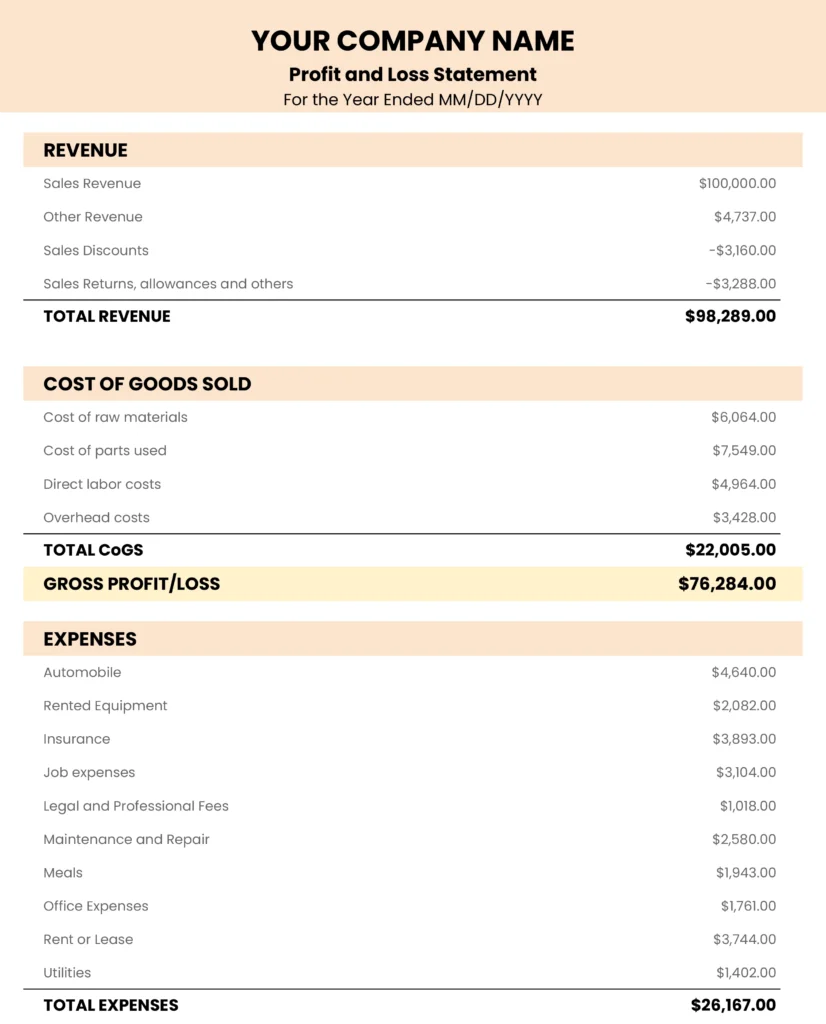
Using a standardized structure offers several advantages, including simplified data entry, reduced errors, and easier comparison across different periods. This consistency allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the financial health of an entity and track performance trends. Furthermore, it streamlines the reporting process, saving valuable time and resources.

Understanding the structure and utility of such reports is crucial for effective financial management. The following sections will explore the key components, various applications, and best practices for creating and utilizing these valuable tools.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are essential for year-to-date statement templates. Consistency in structure ensures data comparability across different periods and departments. A defined layout simplifies data entry and reduces the risk of errors, leading to more accurate and reliable reports. For instance, a standardized balance sheet template always presents assets, liabilities, and equity in the same order, regardless of the reporting period. This allows for straightforward analysis of financial position changes over time.
This structured approach also benefits stakeholders. Analysts, investors, and management can readily interpret information presented in a familiar format, facilitating informed decision-making. Consistent terminology and data presentation minimize ambiguity and enhance clarity. Consider a standardized income statement template. Regardless of fluctuations in revenue or expenses, the consistent presentation of gross profit, operating income, and net income allows for immediate identification of performance trends. This enables proactive responses to changes in the business environment.
Ultimately, a standardized format contributes to the integrity and utility of year-to-date statements. It promotes transparency, improves efficiency, and enhances the value of financial reporting. While specific data points may vary, the consistent structure provides a reliable framework for understanding financial performance. This understanding is fundamental to effective resource allocation and strategic planning.
2. Current Year Data
Current year data forms the core of a year-to-date statement template. The template serves as a structure to organize and present financial information accumulated from the start of the fiscal year up to the present date. Without current year data, the template remains an empty framework, devoid of actionable insights. This data provides a real-time snapshot of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making based on the most recent information. For example, a year-to-date income statement populated with current year revenue and expense figures allows businesses to track profitability trends and adjust strategies accordingly. Similarly, a balance sheet reflecting current assets and liabilities provides a clear picture of the current financial position.
The inclusion of current year data allows for meaningful comparisons and analysis. By comparing current year-to-date performance with previous periods or projected targets, stakeholders can identify areas of strength and weakness, assess progress toward goals, and make necessary adjustments. Consider a retail business tracking year-to-date sales figures. Comparing these figures against the same period in the previous year reveals growth trends and potential market shifts. This information can inform inventory management, marketing campaigns, and overall business strategy.
Accurate and up-to-date data is crucial for sound financial management. Challenges may arise from data entry errors, system integration issues, or delays in data collection. Overcoming these challenges through robust data management processes and system automation ensures the reliability and timeliness of year-to-date statements. Ultimately, the effective utilization of current year data within a well-designed template provides valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and contribute to financial success.
3. Key Performance Indicators
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential components of a year-to-date statement template. They provide quantifiable metrics that track progress towards specific objectives and offer insights into an organization’s financial health and operational efficiency. KPIs within a year-to-date context allow for ongoing performance monitoring throughout the fiscal year, enabling timely interventions and adjustments to strategies. The selection of relevant KPIs depends on the specific industry, organizational goals, and the nature of the financial statement. For example, a sales-focused business might track year-to-date revenue growth, average transaction value, and customer acquisition cost as key indicators of sales performance. A manufacturing company, on the other hand, might prioritize KPIs such as year-to-date production output, unit cost, and inventory turnover.
The inclusion of KPIs in a year-to-date statement template facilitates performance evaluation and informed decision-making. By tracking KPIs over time, stakeholders gain a clear understanding of trends and patterns, enabling proactive responses to changing market conditions or internal challenges. For instance, a decline in year-to-date gross profit margin could signal pricing pressures or rising production costs, prompting management to explore cost-cutting measures or pricing adjustments. Conversely, a consistent increase in year-to-date customer retention rate could validate the effectiveness of customer loyalty programs and inform future marketing strategies. Visual representations of KPIs, such as charts and graphs within the template, further enhance understanding and communication of performance trends.
Effective utilization of KPIs requires careful selection, consistent measurement, and accurate data. Challenges may arise from data inconsistencies, inadequate tracking mechanisms, or the selection of irrelevant metrics. Overcoming these challenges through robust data management practices and clearly defined performance targets ensures that KPIs provide meaningful insights. Ultimately, the integration of relevant KPIs within a year-to-date statement template empowers organizations to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions that contribute to achieving strategic objectives.
4. Comparison Capabilities
Effective financial analysis relies heavily on the ability to compare performance across different periods. A year-to-date statement template, by its very nature, facilitates such comparisons, providing a structured framework for evaluating current performance against prior periods, budgets, or industry benchmarks. This comparative analysis unlocks valuable insights into trends, identifies potential issues, and informs strategic adjustments.
- Previous Period ComparisonComparing current year-to-date figures with those from the same period in the previous year reveals growth patterns and performance changes. This historical context helps identify seasonal trends, assess the impact of market fluctuations, and evaluate the effectiveness of implemented strategies. For example, comparing year-to-date sales figures can highlight whether revenue growth is accelerating or decelerating compared to the prior year, offering valuable insights for sales forecasting and inventory management.
- Budgetary ComparisonComparing year-to-date actual results against the budgeted figures reveals variances and provides insights into budgetary adherence. This analysis allows for timely identification of deviations from planned performance, enabling corrective actions to be taken. For instance, if year-to-date expenses consistently exceed the budget, it signals a need to review spending patterns and implement cost-control measures.
- BenchmarkingComparing year-to-date performance against industry benchmarks or competitors’ data offers a broader perspective on an organization’s standing within the market. This external comparison helps identify areas of competitive advantage or disadvantage, informing strategic initiatives aimed at enhancing market positioning. For example, a company with a higher year-to-date profit margin than its industry average may indicate operational efficiency and effective cost management.
- Trend AnalysisAnalyzing year-to-date data across multiple reporting periods facilitates the identification of ongoing trends. This reveals consistent patterns in financial performance, enabling more accurate forecasting and proactive adjustments to strategy. For instance, consistently increasing year-to-date customer acquisition costs could indicate a need to re-evaluate marketing strategies or explore alternative customer acquisition channels.
The comparison capabilities inherent within a year-to-date statement template transform raw financial data into actionable insights. By facilitating various comparisons, the template empowers stakeholders to understand performance trends, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions that drive financial success. This ability to analyze performance in context is crucial for effective financial management and strategic planning.
5. Concise Presentation
Clarity and efficiency are paramount in financial reporting. Concise presentation within a year-to-date statement template ensures data is easily digestible and key insights are readily apparent. Avoiding unnecessary clutter and focusing on essential information enhances understanding and facilitates informed decision-making. A concisely presented statement maximizes impact while minimizing the time required for interpretation.
- Data Aggregation and SummarizationStrategic aggregation and summarization of data prevent information overload. Rather than presenting every individual transaction, data is grouped into meaningful categories and summarized at appropriate levels. For example, instead of listing every sale individually, a year-to-date sales report might summarize sales by product category or region. This approach provides a clear overview of performance without overwhelming the reader with granular detail.
- VisualizationsCharts, graphs, and other visual aids enhance understanding and highlight key trends. Visual representations of year-to-date data allow stakeholders to quickly grasp performance patterns and identify areas requiring attention. For instance, a line graph depicting year-to-date revenue trends can readily reveal growth patterns or seasonal fluctuations, providing insights that might be missed in a purely numerical presentation.
- Clear and Consistent LabelingClear and consistent labeling of data points, axes, and sections within the template ensures unambiguous interpretation. Using standardized terminology and definitions eliminates confusion and promotes accurate analysis. For example, consistently labeling revenue as “Net Sales” throughout the year-to-date income statement prevents misinterpretations and ensures data comparability across different periods.
- Strategic Use of White SpaceEffective use of white space improves readability and prevents the template from appearing cluttered. Adequate spacing between sections, data points, and visual elements enhances visual appeal and allows the reader to easily navigate the information. This contributes to a more positive user experience and encourages thorough review of the presented data.
Concise presentation transforms complex financial data into an easily digestible format. Within a year-to-date statement template, it ensures that stakeholders can quickly grasp key performance indicators, identify trends, and make informed decisions. This focus on clarity and efficiency maximizes the value of the financial reporting process and contributes to effective financial management.
Key Components of a Year-to-Date Statement Template
A well-structured template ensures clarity, accuracy, and comparability in financial reporting. Several key components contribute to the effectiveness of a year-to-date statement template.
1. Reporting Period: Clearly defined start and end dates establish the scope of the data presented. This ensures all figures reflect the same period, enabling accurate comparisons and trend analysis.
2. Identification Information: Entity name, reporting unit, and relevant contact information provide context and ensure the report is readily identifiable. This information is crucial for proper record-keeping and communication.
3. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Relevant KPIs offer quantifiable metrics to assess performance against objectives. These metrics, such as revenue, expenses, or profit margins, provide a snapshot of financial health and operational efficiency.
4. Current Year-to-Date Figures: Actual financial results accumulated from the beginning of the fiscal year to the present date form the core of the statement. This data allows stakeholders to assess current performance.
5. Prior Year-to-Date Figures: Including data from the same period in the previous year allows for year-over-year comparisons. This historical context reveals growth trends, assesses the impact of market changes, and evaluates the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
6. Budget or Target Figures: Comparing year-to-date actuals against budgeted or target figures reveals variances and insights into budgetary adherence. This analysis facilitates timely corrective actions and resource allocation decisions.
7. Variance Analysis: Calculating and presenting the difference between actual results and budget/target figures provides a clear picture of performance deviations. This highlights areas requiring attention and informs corrective strategies.
8. Commentary and Analysis: A concise narrative explaining significant variances, trends, or noteworthy observations provides valuable context and insights. This qualitative analysis complements the quantitative data, enabling a deeper understanding of performance drivers.
These elements ensure the template provides a comprehensive and informative overview of year-to-date financial performance, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
How to Create a Year-to-Date Statement Template
Creating a robust year-to-date statement template requires careful planning and consideration of key elements. A well-structured template ensures clarity, accuracy, and comparability in financial reporting.
1. Define the Scope and Purpose: Clearly outline the specific financial information to be included and the intended audience. This clarifies the template’s objective and ensures relevant data is captured.
2. Determine Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Select relevant KPIs that align with organizational goals and provide meaningful insights into performance. These metrics will form the core data points within the template.
3. Choose a Reporting Period: Establish consistent reporting periods (e.g., monthly, quarterly) and define the start and end dates for the year-to-date calculations. This ensures data consistency and comparability.
4. Design the Template Layout: Structure the template with clear sections for identification information, KPIs, current year-to-date figures, prior year-to-date figures, budget/target figures, variance analysis, and commentary. Consider using tables, charts, and other visual aids to enhance readability.
5. Establish Data Sources: Identify the systems or sources from which data will be extracted. Ensure data accuracy and establish processes for regular updates to maintain current information.
6. Implement Formulas and Calculations: Incorporate formulas and automated calculations within the template to derive key metrics, such as variances and percentages. This reduces manual effort and minimizes the risk of errors.
7. Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the template with sample data to ensure accuracy and functionality. Solicit feedback from stakeholders and refine the template based on their input.
8. Document and Train: Provide clear documentation on how to use and interpret the template. Train relevant personnel on data entry, reporting procedures, and interpretation of results.
A well-designed template provides a structured framework for tracking year-to-date financial performance, facilitating informed decision-making and contributing to organizational success. Consistent application and regular review of the template ensures its ongoing effectiveness.
Accurate and accessible financial information is crucial for effective decision-making. A well-designed year-to-date statement template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting key financial data, enabling stakeholders to monitor performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Standardized formats, clear KPIs, and comparison capabilities enhance the template’s utility, facilitating efficient analysis and communication. From defining scope and purpose to data sourcing and visualization, careful consideration of each component contributes to the template’s overall effectiveness.
Effective financial management hinges on the ability to extract actionable insights from data. Leveraging a robust year-to-date statement template empowers organizations to gain a clear understanding of their financial performance and make data-driven decisions that contribute to long-term success. Regular review and refinement of the template, coupled with consistent data management practices, ensure its ongoing value as a critical tool for financial analysis and strategic planning.


