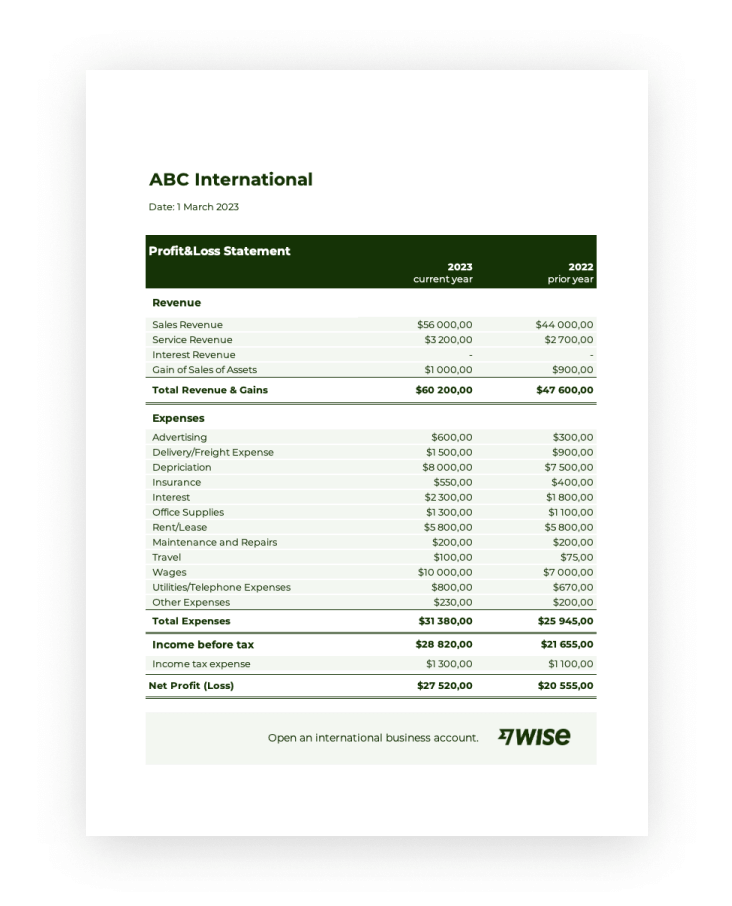
Utilizing a standardized structure for this annual report offers several advantages. It facilitates consistent tracking of financial data, enabling year-over-year comparisons and trend analysis. A well-designed format simplifies the process of preparing the report, reducing the likelihood of errors and omissions. Furthermore, a readily available framework ensures compliance with accounting standards and allows stakeholders, such as investors and lenders, to easily understand and analyze the organization’s financial health.

Understanding the components and significance of this financial summary is essential for effective financial management. The following sections will delve deeper into the specific elements of a typical report, exploring best practices for its creation and utilization in informed decision-making.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are crucial for yearly profit and loss statement templates. Consistency ensures data integrity and facilitates meaningful comparisons across reporting periods. A standardized structure outlines specific sections for revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income, ensuring all essential financial data is captured systematically. This consistency enables trend analysis, performance evaluation, and informed decision-making based on reliable and comparable financial information. Without a standardized format, comparing financial performance across different periods becomes challenging, hindering effective analysis and strategic planning.
Consider a business comparing its performance over several years. With a standardized profit and loss template, changes in gross profit margin or operating expenses become readily apparent. This clarity allows management to pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, identify potential cost-saving measures, and track the effectiveness of strategic initiatives. For example, a consistent increase in operating expenses as a percentage of revenue might signal inefficiencies requiring attention. Conversely, a steady growth in net income demonstrates the positive impact of strategic decisions. This level of insight is only possible with a standardized framework.
Standardization within financial reporting provides a clear and concise overview of financial performance, promoting transparency and accountability. It simplifies audits, streamlines communication with stakeholders, and facilitates benchmarking against industry averages. While specific line items might vary depending on industry or business model, adherence to a standardized framework ensures consistent data presentation, contributing to a more accurate and insightful understanding of financial health and long-term sustainability. Navigating the complexities of financial analysis requires a robust foundation, and a standardized profit and loss statement template provides precisely that.
2. Annual Financial Overview
A comprehensive annual financial overview is intrinsically linked to a well-structured yearly profit and loss statement template. The template serves as the foundation upon which the annual overview is built, providing a standardized framework for organizing and presenting key financial data. This structured presentation allows for a clear understanding of financial performance over the course of a fiscal year, revealing profitability, revenue streams, cost structures, and overall financial health. Without such a template, creating a meaningful annual overview becomes significantly more challenging. The template ensures consistency in data presentation, facilitating year-over-year comparisons and trend analysis, both essential for a robust annual overview.
Consider a retail business aiming to assess its annual performance. A yearly profit and loss statement template would categorize data into sections like sales revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses (rent, salaries, marketing), and net income. This categorization allows for a granular understanding of the business’s financial drivers. For instance, if sales revenue increased but net income remained stagnant or declined, the annual overview, drawing data from the template, might reveal increased operating expenses as the culprit. Perhaps marketing costs rose significantly or rent in a new location proved more expensive than anticipated. These insights, gleaned from the structured data within the template, form the core of the annual financial overview, enabling informed decision-making for the subsequent year.
The practical significance of this connection lies in its ability to inform strategic planning and resource allocation. By analyzing the annual overview derived from the profit and loss template, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize cost structures, and develop strategies for future growth. Challenges may arise in accurately capturing and categorizing all relevant financial data. However, consistent use of a comprehensive template mitigates this risk, ensuring data integrity and reliability. Ultimately, the symbiotic relationship between a yearly profit and loss statement template and the annual financial overview it generates empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of financial management and achieve long-term sustainability.
3. Performance Tracking
Effective performance tracking relies heavily on the structured data provided by a yearly profit and loss statement template. This template acts as a repository for key financial metrics, enabling systematic monitoring of performance over time. Without a consistent framework for data collection and presentation, performance tracking becomes fragmented and unreliable, hindering the ability to identify trends, assess progress toward goals, and make informed decisions. The template provides the necessary structure for meaningful performance analysis, allowing organizations to gain valuable insights into their financial health and operational efficiency.
- Trend AnalysisTrend analysis, a cornerstone of performance tracking, becomes significantly more manageable with the consistent data structure offered by a yearly profit and loss statement template. By comparing key financial metrics across multiple reporting periods, organizations can identify upward or downward trends in areas such as revenue growth, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. For example, consistent growth in revenue coupled with a stable or declining cost of goods sold signals improved profitability. Conversely, a steady increase in operating expenses without a corresponding rise in revenue could indicate operational inefficiencies. These insights, derived from trend analysis, empower organizations to proactively address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
- BenchmarkingBenchmarking, a critical component of performance tracking, leverages the standardized format of a yearly profit and loss statement template to compare an organization’s financial performance against industry averages or competitors. By aligning key metrics, such as profit margins and return on assets, with industry benchmarks, organizations gain a clear understanding of their relative performance. This comparison reveals areas where the organization excels and where improvements are needed. For instance, a lower-than-average profit margin might suggest inefficiencies in production or pricing strategies, prompting further investigation and corrective action. The template facilitates this comparative analysis by providing a consistent structure for data extraction and comparison.
- Goal Setting and MeasurementThe structured data within a yearly profit and loss statement template provides a clear foundation for establishing and measuring financial goals. By analyzing historical performance data captured within the template, organizations can set realistic and achievable targets for revenue growth, cost reduction, and profitability. The template also facilitates ongoing monitoring of progress towards these goals. Regular review of the profit and loss statement allows organizations to track performance against targets, identify any deviations, and implement corrective measures as needed. For example, if revenue growth falls short of projections, the organization can analyze the underlying causes, such as declining market share or ineffective marketing campaigns, and adjust strategies accordingly. The template ensures that goal setting and measurement are based on consistent and reliable data, enhancing the effectiveness of performance management.
- Resource AllocationEffective resource allocation hinges on a clear understanding of financial performance, facilitated by a yearly profit and loss statement template. By analyzing revenue streams, cost structures, and profitability metrics within the template, organizations can identify areas where resources are being utilized effectively and where adjustments are needed. For example, if a particular product line consistently generates losses, the organization might consider discontinuing it and reallocating resources to more profitable ventures. Conversely, strong performance in a specific area could justify increased investment to further capitalize on its growth potential. The template provides the data-driven insights necessary to make informed decisions about resource allocation, optimizing the use of capital and maximizing return on investment.
The interconnectedness of these facets of performance tracking underscores the vital role of a yearly profit and loss statement template. The template provides the structured data necessary for trend analysis, benchmarking, goal setting, and resource allocation. Consistent use of this template ensures that performance tracking is based on reliable and comparable data, enabling organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions that drive long-term success. Without this structured approach, performance tracking becomes a fragmented and less effective process, limiting the organization’s ability to achieve its financial objectives.
4. Comparability
Comparability, a cornerstone of financial analysis, relies heavily on the consistent structure provided by a yearly profit and loss statement template. This template ensures that financial data is presented in a standardized format across different reporting periods, facilitating meaningful comparisons and trend identification. Without this standardized structure, analyzing performance over time becomes challenging, hindering the ability to assess progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed strategic decisions. The template’s consistent categorization of revenues, expenses, and net income provides the foundation for accurate and reliable comparative analysis.
Consider a manufacturing company analyzing its gross profit margin over several years. Utilizing a consistent yearly profit and loss statement template ensures that cost of goods sold and revenue are calculated and presented uniformly each year. This consistency allows for a direct comparison of gross profit margins, revealing whether profitability is improving or declining. Without a standardized template, changes in calculation methods or data presentation could obscure the true trend, leading to inaccurate conclusions and potentially misguided decisions. For example, if the company changed its method of accounting for inventory costs in one year, the resulting change in cost of goods sold might appear as a significant improvement in gross margin, even if actual production efficiency remained unchanged. A consistent template prevents such distortions, enabling accurate performance evaluation.
The practical significance of comparability within financial analysis lies in its capacity to inform strategic decision-making. By comparing performance across different periods, businesses can identify trends, assess the effectiveness of strategic initiatives, and make data-driven adjustments to optimize future performance. Challenges might arise in maintaining absolute consistency, particularly when accounting standards change or businesses evolve. However, a well-designed yearly profit and loss statement template mitigates this risk by providing a framework that adapts to these changes while preserving comparability. Ultimately, the ability to compare financial data accurately and reliably empowers organizations to track progress, identify opportunities, and navigate the complexities of the business environment with greater confidence.
5. Key Financial Metrics
A yearly profit and loss statement template serves as the primary source for extracting key financial metrics crucial for evaluating an organization’s financial performance. These metrics provide quantifiable insights into profitability, operational efficiency, and overall financial health. Without a structured template, extracting and analyzing these metrics becomes significantly more challenging, hindering the ability to make informed business decisions.
- RevenueRevenue, representing the total income generated from sales of goods or services, forms the foundation of the profit and loss statement. A template ensures consistent reporting of revenue, enabling accurate tracking of sales performance over time. For example, comparing revenue figures year-over-year reveals growth trends, identifies seasonal patterns, and provides a basis for future sales projections. Understanding revenue streams is fundamental to assessing financial viability and planning for sustainable growth.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by a company. A standardized template ensures consistent calculation and reporting of COGS, enabling accurate gross profit margin analysis. Tracking COGS helps identify potential cost-saving opportunities within the production process, such as optimizing material usage or improving manufacturing efficiency. For example, a rising COGS as a percentage of revenue could indicate issues with supplier pricing or production inefficiencies, prompting further investigation.
- Operating ExpensesOperating expenses encompass all costs incurred in running a business, excluding COGS. A detailed profit and loss template categorizes these expenses (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing), enabling analysis of spending patterns and identification of areas for potential cost reduction. For example, consistently high marketing expenses coupled with stagnant revenue growth might suggest the need to re-evaluate marketing strategies. Controlling operating expenses is critical for maintaining profitability and achieving financial stability.
- Net IncomeNet income, the bottom line of the profit and loss statement, represents the profit remaining after deducting all expenses from revenue. This crucial metric reflects the overall profitability of the business. Consistent reporting within a template allows for accurate tracking of net income trends over time, providing insights into the effectiveness of business strategies and operational efficiency. Consistent growth in net income indicates financial health and sustainable growth, while declining net income signals potential challenges requiring immediate attention.
These interconnected metrics, derived from a structured yearly profit and loss statement template, provide a comprehensive view of financial performance. Analyzing these metrics individually and collectively enables informed decision-making regarding pricing strategies, cost control measures, investment decisions, and overall business strategy. The template ensures data integrity and comparability, making it an indispensable tool for effective financial management and long-term success.
Key Components of a Yearly Profit and Loss Statement Template
Essential components comprise a robust yearly profit and loss statement template. These elements provide a structured framework for capturing and presenting crucial financial data, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
1. Revenue: Encompasses all income generated from business operations, including sales of goods or services. Accurate revenue reporting is fundamental for assessing financial performance and projecting future growth. Different revenue streams should be clearly delineated within the template.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit margin and identifying potential cost-saving opportunities within the production process. The template should clearly distinguish between direct and indirect costs.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue minus COGS. This metric reflects the profitability of core business operations before considering operating expenses. Gross profit trends provide insights into pricing strategies and production efficiency.
4. Operating Expenses: Include all costs associated with running the business, excluding COGS. These expenses are typically categorized within the template (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing) to facilitate analysis of spending patterns and identify areas for potential cost optimization. Clear categorization allows for better cost control and resource allocation.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit minus Operating Expenses. This metric reflects the profitability of the business after accounting for all operating costs. Tracking operating income trends provides insights into overall operational efficiency and the effectiveness of cost management strategies.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section captures income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time expenses. Accurate reporting of these items provides a complete picture of the organization’s financial performance beyond core operations.
7. Income Tax Expense: Represents the tax liability incurred on taxable income. Accurate calculation and reporting of income tax expense are crucial for compliance and for understanding the true net profitability of the business. The template should reflect applicable tax rates and regulations.
8. Net Income: Calculated as Operating Income plus Other Income/Expenses less Income Tax Expense. This crucial bottom-line metric reflects the overall profitability of the business after accounting for all revenues and expenses. Consistent tracking of net income is essential for assessing financial health and evaluating the success of business strategies.
A comprehensive analysis of these interconnected components, presented within a standardized yearly profit and loss statement template, provides a robust understanding of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning for long-term success.
How to Create a Yearly Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a robust template for an annual profit and loss statement involves several key steps. A well-structured template ensures consistent data capture, facilitates accurate analysis, and supports informed decision-making.
1. Define Reporting Period: Specify the precise start and end dates for the fiscal year. Consistent reporting periods are crucial for year-over-year comparisons and trend analysis. Clarity in the reporting period ensures data integrity and facilitates accurate performance evaluation.
2. Establish Chart of Accounts: Develop a comprehensive chart of accounts that categorizes all revenue and expense items. A well-defined chart of accounts ensures consistent data classification, simplifies data entry, and facilitates detailed analysis of financial performance. This structured approach promotes accuracy and transparency in financial reporting.
3. Design Template Structure: Structure the template with clear sections for revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income. A logical structure ensures all essential financial data is captured systematically, facilitating easy interpretation and analysis. Consider including subcategories within each section for more granular reporting.
4. Incorporate Formulas and Calculations: Integrate formulas to automate calculations, such as gross profit, operating income, and net income. Automated calculations reduce the risk of manual errors, ensure accuracy, and save time during report preparation. Regularly review and update formulas to reflect any changes in accounting standards or business practices.
5. Data Input and Validation: Establish clear procedures for data input and validation to ensure data accuracy and integrity. Regular data validation checks minimize errors and ensure the reliability of financial reports. Consider implementing automated validation rules to prevent inconsistencies and improve data quality.
6. Review and Refinement: Periodically review and refine the template to ensure it remains aligned with evolving business needs and accounting standards. Regular review ensures the template remains relevant, accurate, and effective in supporting financial analysis and decision-making. Seek feedback from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement.
A well-designed template, incorporating these elements, provides a robust framework for capturing, analyzing, and interpreting financial data, enabling informed decision-making and contributing to long-term financial success. Consistent use of a standardized template promotes transparency, facilitates comparability, and supports effective financial management.
A yearly profit and loss statement template provides a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Its standardized structure enables consistent tracking of revenue, costs, and expenses, facilitating clear analysis of profitability and operational efficiency. From revenue streams and cost of goods sold to operating expenses and net income, the template organizes key financial metrics, allowing for meaningful comparisons across reporting periods and informed decision-making. Effective utilization of this template empowers organizations to identify trends, benchmark against industry averages, set realistic financial goals, and allocate resources strategically.
Mastering financial analysis requires a structured approach. A well-designed yearly profit and loss statement template serves as an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of financial management. By leveraging the insights derived from this structured data, organizations gain a deeper understanding of their financial health, enabling them to adapt to market dynamics, optimize performance, and achieve long-term sustainability. Consistent and accurate financial reporting, facilitated by a robust template, forms the bedrock of sound financial management and contributes significantly to informed strategic planning and sustainable growth.


