Utilizing a standardized format for this annual financial report offers several advantages. It ensures consistency and comparability of data year over year, facilitating trend analysis and performance tracking. A pre-designed structure streamlines the reporting process, reducing the time and effort required for preparation. Moreover, it promotes transparency and clarity, making the financial information readily accessible and understandable to all stakeholders.

This overview sets the stage for a deeper exploration of specific elements within the annual financial statement. The following sections will delve into the key components, including revenue streams, expense categories, and the calculation of net income or loss. Further discussion will address the interpretation of this financial data and its implications for future business strategies.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is crucial for yearly profit and loss statements. Consistency in presentation allows for straightforward comparison of financial data across different periods, facilitating trend analysis and informed decision-making. A standardized template ensures key financial elements, such as revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income, are presented in the same order and manner each year. This eliminates ambiguity and allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the company’s financial performance and trajectory. For example, consistent categorization of operating expenses allows for accurate tracking of changes in research and development spending or marketing costs over time.
Without a standardized format, analyzing financial performance becomes significantly more challenging. Variability in presentation can obscure trends and make it difficult to identify areas of improvement or concern. Imagine comparing two profit and loss statements, one categorizing marketing expenses under “Selling Expenses” and the other under “Administrative Expenses.” This inconsistency hinders direct comparison and requires additional effort to reconcile the data. A standardized template mitigates these challenges, promoting transparency and facilitating efficient analysis. Standardization also simplifies auditing processes and ensures compliance with reporting regulations.
In conclusion, a standardized format is not merely a matter of aesthetics; it is fundamental to the utility and interpretability of yearly profit and loss statements. It empowers stakeholders with clear, consistent, and comparable financial information, enabling them to make informed decisions based on reliable data. This structured approach fosters transparency, accountability, and ultimately, contributes to sound financial management and growth.
2. Annual Reporting
Annual reporting provides a comprehensive yearly overview of an organization’s financial performance, and a yearly profit and loss statement template serves as a crucial tool in this process. This structured reporting is essential for internal management, investors, and other stakeholders to assess financial health, track progress, and make informed decisions.
- Financial Record KeepingMeticulous record-keeping throughout the year forms the foundation for accurate annual reporting. Each transaction, whether revenue or expense, must be accurately documented and categorized. A yearly profit and loss statement template provides the framework for organizing this data, ensuring consistency and facilitating the generation of meaningful reports. For example, detailed records of sales transactions are essential for accurately reporting annual revenue.
- Performance EvaluationAnnual reports, including profit and loss statements, enable businesses to evaluate their financial performance against predefined goals and industry benchmarks. This analysis provides insights into areas of strength and weakness, informing strategic adjustments for the following year. For instance, comparing actual operating expenses to budgeted figures can reveal inefficiencies or areas for cost optimization.
- Stakeholder CommunicationAnnual reports serve as a primary communication tool for conveying financial performance to stakeholders. Investors, lenders, and regulatory bodies rely on this information to assess financial health and make informed decisions. A clear and concise profit and loss statement, generated using a standard template, enhances transparency and facilitates understanding. For example, a consistently formatted income statement builds trust with investors by providing a clear view of profitability trends.
- Strategic PlanningThe insights gained from annual reports, particularly the profit and loss statement, inform strategic planning for the subsequent year. By analyzing past performance, businesses can identify growth opportunities, anticipate potential challenges, and adjust their strategies accordingly. For instance, consistent losses in a particular product line, as revealed in the profit and loss statement, might lead to a decision to discontinue that product.
In conclusion, annual reporting, facilitated by a yearly profit and loss statement template, provides a critical mechanism for evaluating past performance, communicating financial health to stakeholders, and informing future strategic decisions. The structured approach inherent in utilizing a template ensures consistency, accuracy, and transparency, contributing to sound financial management and long-term sustainability.
3. Financial Performance
Financial performance represents the overall economic outcome of an organization over a specific period. A yearly profit and loss statement template provides the structured framework for capturing, analyzing, and communicating this performance. The statement systematically presents revenues, expenses, and the resulting net income or loss, offering a concise yet comprehensive view of financial health. This structured presentation facilitates the assessment of profitability, operational efficiency, and overall financial stability. For example, a consistent decline in net income over several years, as revealed through consistent application of the template, signals underlying issues requiring attention. Conversely, steady revenue growth and controlled expenses, evident in the statement, demonstrate effective management and positive financial trajectory.
Analyzing financial performance through a standardized yearly statement allows stakeholders to identify trends and make data-driven decisions. Comparing performance year-over-year reveals patterns in revenue generation, cost management, and profitability. This analysis informs strategic planning, resource allocation, and operational adjustments. For instance, if the statement reveals escalating operating expenses relative to revenue growth, management can investigate the cause and implement cost-control measures. Furthermore, consistent application of the template allows for benchmarking against competitors and industry averages, providing valuable context for evaluating performance. A company consistently outperforming its competitors in key metrics, as demonstrated by comparative analysis using the template, signals a strong competitive advantage.
Understanding financial performance is crucial for long-term sustainability and growth. The yearly profit and loss statement, generated through a standardized template, provides the necessary insights for informed decision-making. It enables organizations to identify areas for improvement, capitalize on strengths, and adapt to changing market conditions. Challenges such as declining profitability or rising expenses can be addressed proactively through strategic interventions based on the insights derived from the statement. Ultimately, the consistent and structured approach to tracking and analyzing financial performance, facilitated by the yearly profit and loss statement template, contributes to sound financial management and long-term success. This understanding empowers stakeholders to navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and achieve sustained financial health.
4. Revenue & Expenses
Revenue and expenses are the fundamental components of a yearly profit and loss statement template. Their accurate recording and categorization are essential for determining profitability and assessing financial performance. A clear understanding of these elements is crucial for interpreting the statement and making informed business decisions. This section explores the facets of revenue and expenses within the context of a standardized yearly profit and loss statement.
- Revenue StreamsRevenue represents income generated from a company’s primary business activities. A yearly profit and loss statement template typically categorizes revenue streams for a more granular analysis. For a manufacturing company, this might include sales of finished goods, service fees, and licensing revenue. Understanding the contribution of each revenue stream provides insights into business performance and helps identify growth opportunities. For example, a decline in sales revenue from a core product line might signal a need for product innovation or marketing adjustments. Accurately capturing and categorizing revenue is crucial for determining overall profitability and making informed decisions regarding resource allocation and future strategy.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by a company. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Within the yearly profit and loss statement template, COGS is subtracted from revenue to determine gross profit. Analyzing COGS helps assess production efficiency and pricing strategies. For example, a rising COGS without a corresponding increase in sales price could erode profit margins, indicating a need to streamline production processes or negotiate better supplier agreements.
- Operating ExpensesOperating expenses encompass the costs incurred in running the business outside of direct production. These include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative expenses. The yearly profit and loss statement template details these expenses, often categorizing them for deeper analysis. Tracking operating expenses is critical for identifying areas of potential cost optimization and ensuring efficient resource allocation. For example, significant increases in marketing spend without a corresponding rise in sales revenue may necessitate a review of marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Non-Operating ExpensesNon-operating expenses are costs unrelated to core business operations, such as interest payments on debt or losses from asset sales. These are typically listed separately within the yearly profit and loss statement template. Understanding non-operating expenses provides a complete picture of financial performance and helps evaluate the impact of financial decisions unrelated to core operations. For example, high interest expense due to substantial debt could significantly impact profitability, highlighting the need for debt management strategies.
By systematically categorizing and presenting revenue and expenses, the yearly profit and loss statement template provides a crucial tool for analyzing financial performance. Understanding the relationship between these elements and their impact on profitability empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost management, resource allocation, and overall business strategy. Analyzing trends in revenue and expenses over time, facilitated by the consistent format of the template, allows for proactive adjustments and contributes to long-term financial health and sustainability.
5. Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis, a critical component of financial assessment, relies heavily on the data presented within a yearly profit and loss statement template. This structured financial report provides the foundational information necessary to assess a company’s ability to generate profit over a specific period. The standardized format ensures consistency in data presentation, facilitating trend analysis and comparison across different periods. The statement systematically categorizes revenue streams, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other relevant financial figures. This structured presentation allows analysts to calculate key profitability metrics, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. These metrics provide insights into the efficiency of operations, pricing strategies, and overall financial health. For example, declining gross profit margins over several years, as revealed through analysis of yearly statements, could indicate increasing production costs or competitive pressures on pricing.
Understanding the relationship between revenue generation and expense management is crucial for effective profitability analysis. A yearly profit and loss statement template facilitates this understanding by presenting these elements in a clear and organized manner. Analyzing trends in revenue growth, cost control, and resulting profit margins allows stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions. For instance, consistent increases in operating expenses without corresponding revenue growth, evident within the yearly statements, signal a need for cost optimization strategies. Furthermore, comparing profitability metrics against industry benchmarks provides valuable context for evaluating performance. A company consistently underperforming its industry peers in net profit margin, as revealed through comparative analysis using the template, suggests potential weaknesses in pricing strategies or cost management.
Effective profitability analysis, facilitated by a yearly profit and loss statement template, provides crucial insights for strategic decision-making. Identifying trends, understanding cost structures, and evaluating profit margins empowers organizations to implement targeted interventions. These interventions might involve streamlining operations, adjusting pricing strategies, or investing in initiatives to boost revenue. The insights gleaned from consistent and structured profitability analysis contribute to sound financial management and long-term sustainability. Ignoring these insights could lead to declining profitability, reduced competitiveness, and ultimately, jeopardize financial health. The yearly profit and loss statement template, therefore, serves as an indispensable tool for informed financial management and strategic planning.
6. Strategic Decision-Making
Strategic decision-making relies heavily on accurate and accessible financial data. A yearly profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting this crucial information, enabling informed decisions that drive business growth and sustainability. The template’s consistent format facilitates trend analysis and performance evaluation, offering valuable insights into revenue streams, cost structures, and overall profitability. This structured approach empowers stakeholders to identify areas for improvement, capitalize on strengths, and adapt to evolving market conditions.
- Resource AllocationEffective resource allocation depends on understanding where investments generate the highest returns. Analysis of a yearly profit and loss statement reveals profitable product lines, efficient departments, and areas requiring additional investment. For example, a product line consistently generating losses, as evident in the statement, might warrant reallocation of resources to more profitable ventures. Conversely, a rapidly growing segment, highlighted by increasing revenue in the statement, might justify increased investment to further accelerate growth.
- Pricing StrategiesPricing decisions significantly impact profitability. Yearly profit and loss statements provide insights into the relationship between pricing, sales volume, and profit margins. For instance, if increasing prices result in declining sales volume and lower overall profit, as revealed in the statement, a price adjustment or alternative pricing strategy may be necessary. Conversely, if the statement shows consistently high profit margins, it might signal an opportunity to increase prices without significantly impacting sales volume.
- Cost ManagementControlling costs is essential for maximizing profitability. Analyzing a yearly profit and loss statement helps identify areas where cost optimization is possible. For example, consistently rising operating expenses without a corresponding increase in revenue, as evident in the statement, might necessitate cost-cutting measures or process improvements. Conversely, if the statement reveals that cost-cutting measures have successfully increased profitability, it validates the effectiveness of those strategies and encourages further exploration of cost optimization opportunities.
- Growth InitiativesStrategic growth initiatives require careful evaluation of potential returns and associated risks. A yearly profit and loss statement provides historical performance data crucial for forecasting future growth and assessing the viability of new ventures. For example, before launching a new product line, analyzing past product launches, as documented in previous statements, can inform projections and risk assessments. Conversely, consistent profitability and strong cash flow, evident in the statement, might provide the financial justification for pursuing expansion opportunities or acquisitions.
The yearly profit and loss statement template, therefore, acts as a crucial tool for strategic decision-making. By providing a structured view of financial performance, it empowers stakeholders to make informed choices regarding resource allocation, pricing strategies, cost management, and growth initiatives. This data-driven approach enhances the probability of success, mitigates risks, and contributes to long-term financial health and sustainable growth. Failing to utilize this information effectively could lead to missed opportunities, inefficient resource allocation, and ultimately, jeopardize long-term viability.
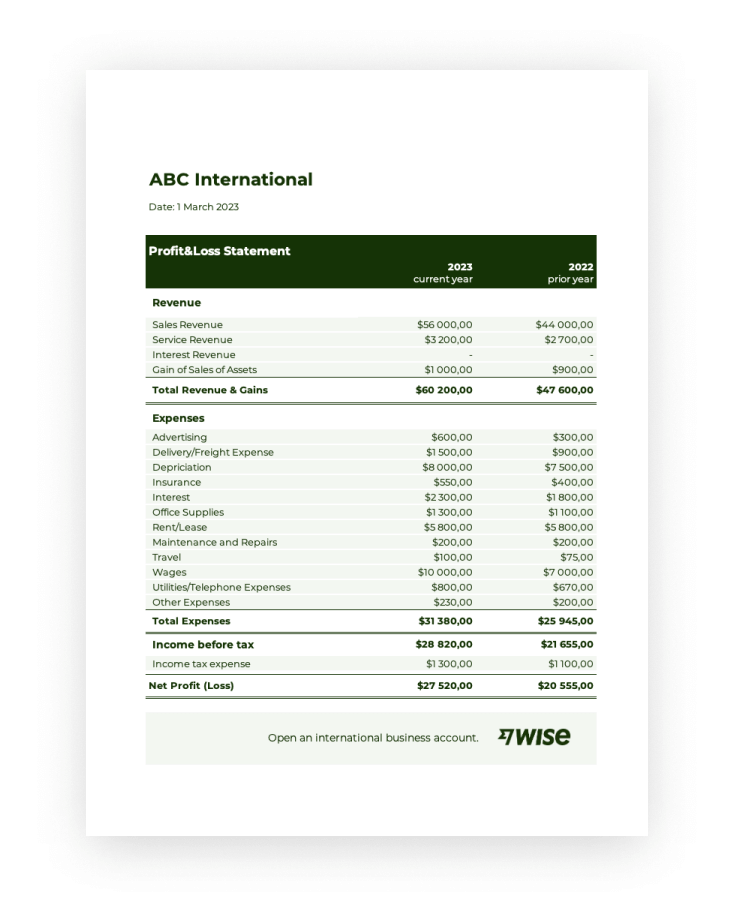
Key Components of a Yearly Profit and Loss Statement Template
A comprehensive understanding of key components within a standardized yearly profit and loss statement is essential for interpreting financial performance and making informed business decisions. These components provide a structured view of revenue generation, cost management, and resulting profitability.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from business operations, often categorized by revenue streams. Accurate revenue recognition is crucial for assessing overall financial performance.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Understanding COGS is essential for calculating gross profit and assessing production efficiency.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue less COGS, gross profit represents the profit generated from core business operations before accounting for operating expenses.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative expenses. Analyzing operating expenses is crucial for identifying areas for potential cost optimization.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit less Operating Expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of core business operations.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section captures income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains, or losses from asset sales.
7. Income Before Taxes: This figure represents the company’s earnings before accounting for income tax expense.
8. Income Tax Expense: This section details the expense associated with corporate income taxes.
9. Net Income: Representing the bottom line, net income is the final profit or loss after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for. This is a key indicator of a company’s overall financial performance and profitability.
Systematic presentation of these components within a standardized template allows for consistent tracking, analysis, and comparison of financial data across different periods. This structured approach facilitates informed decision-making regarding resource allocation, pricing strategies, cost management, and overall business strategy. Accurate data and insightful analysis within this framework are essential for driving sustainable growth and long-term financial health.
How to Create a Yearly Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a standardized yearly profit and loss statement involves a systematic approach to organizing and presenting financial data. This structured format ensures consistency, facilitates analysis, and promotes informed decision-making.
1. Choose a Standardized Template: Selecting a pre-designed template ensures consistency and comparability across reporting periods. Numerous templates are available online or through accounting software. Consistency in formatting facilitates trend analysis and simplifies comparisons.
2. Establish a Consistent Reporting Period: Define a clear 12-month reporting period. This ensures comparability year over year and aligns with standard accounting practices. Consistent reporting periods are crucial for accurate trend analysis.
3. Record Revenue: Meticulously record all revenue generated during the reporting period. Categorize revenue streams for a more granular analysis and identify key drivers of income. Accurate revenue recognition is fundamental to a reliable statement.
4. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Determine the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit and assessing production efficiency.
5. Document Operating Expenses: Record all operating expenses, categorizing them for detailed analysis. This includes expenses such as salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative costs. Categorization facilitates cost management and optimization efforts.
6. Incorporate Other Income and Expenses: Include any non-operating income or expenses, such as interest income or losses from asset sales. This provides a complete picture of financial performance beyond core business operations.
7. Calculate Net Income: Subtract total expenses (COGS, operating expenses, and other expenses) from total revenue to arrive at net income. Net income, or the “bottom line,” represents the overall profit or loss for the reporting period.
8. Review and Verify: Thoroughly review the statement for accuracy and completeness before finalizing. Accurate data is paramount for reliable analysis and informed decision-making. Verification ensures data integrity.
A well-structured yearly profit and loss statement provides a comprehensive overview of financial performance. Consistent application of these steps ensures accuracy, comparability, and valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Systematic utilization of a yearly profit and loss statement template provides invaluable insights into financial performance. Standardized reporting facilitates clear tracking of revenue and expenses, enabling accurate calculation of profit margins and identification of trends. Consistent application of this structured approach fosters data-driven decision-making regarding resource allocation, pricing strategies, cost management, and growth initiatives. Through meticulous record-keeping and comprehensive analysis within this framework, organizations gain a deeper understanding of their financial health, empowering them to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth.
The consistent application of a yearly profit and loss statement template equips stakeholders with the necessary information to navigate the complexities of the business landscape. By fostering transparency and accountability, this structured approach to financial reporting contributes significantly to long-term stability and success. Regular review and analysis of this crucial financial document are essential for informed strategic planning, effective resource management, and the pursuit of sustained financial health. Ultimately, disciplined financial management, guided by the insights gleaned from consistent and accurate reporting, is paramount for achieving long-term objectives and securing a competitive advantage.


